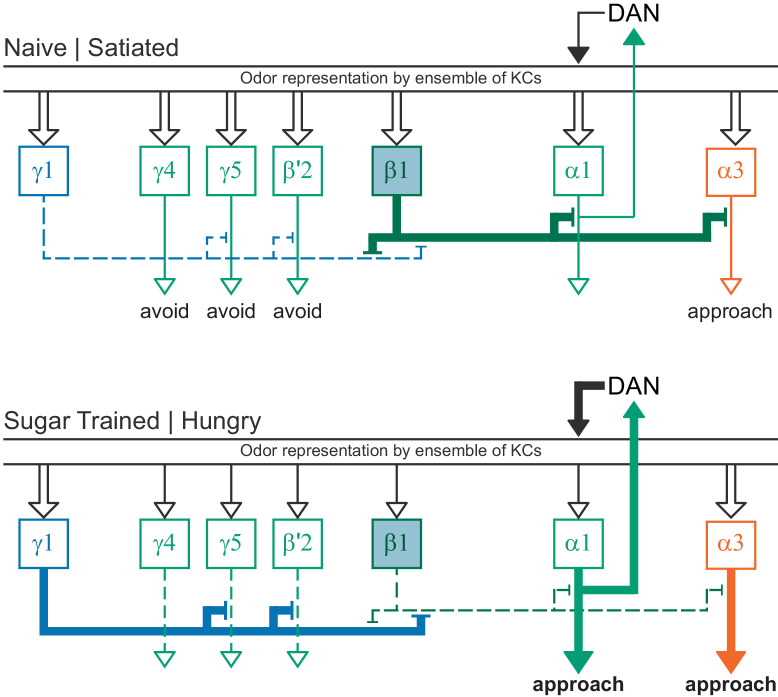
Figure 41. MBON network representation of appetitive memory.
Sugar-responsive DANs innervating γ4, γ5, β′2, and β1 depress odor-specific KC synapses onto the respective MBONs. Depression of the odor-specific response of MBON06 (β1>α) reduces odor-specific feedforward inhibition onto the MBON07 (α1) and MBON14 (α3). This frees α3 to direct odor-driven approach behavior and increases activity in a recurrent α1 MBON07-PAM11aad DAN loop to consolidate long-term appetitive memory. MBON11 (γ1pedc>α/β) is sensitive to satiety state and is more responsive when the fly is hungry. Hunger therefore further promotes appetitive memory formation and expression by increasing inhibition onto MBON01 (γ5β′2a) and β′2 MBONs and by further reducing the feedforward inhibitory effects of MBON06 (β1>α) MBON within α1 and α3. These changes together leave the network in a hunger state-dependent configuration that directs strong odor-specific approach behavior.