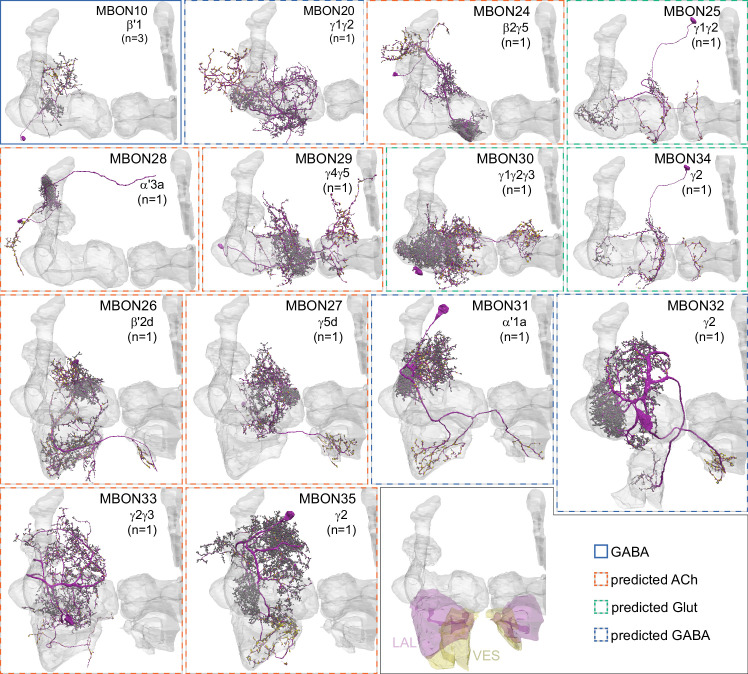
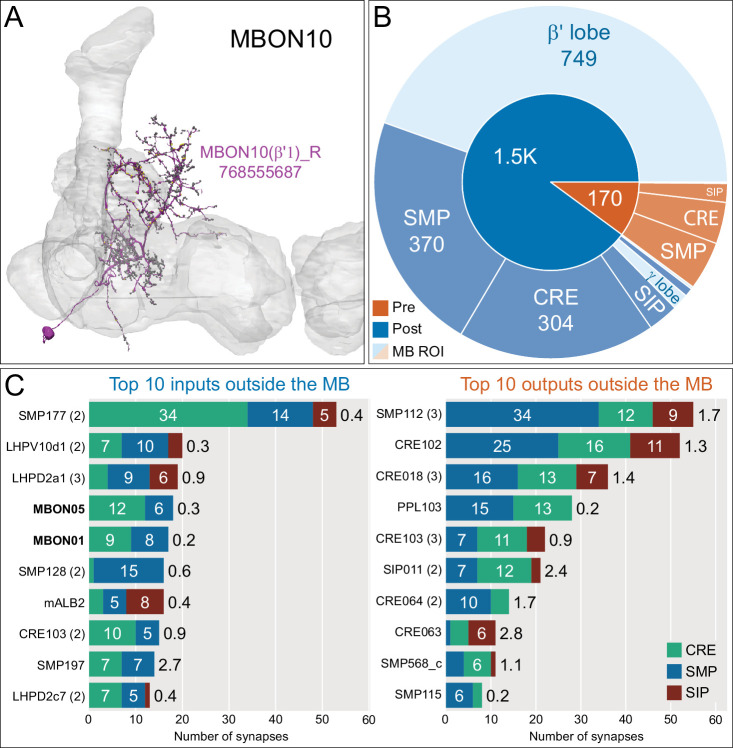
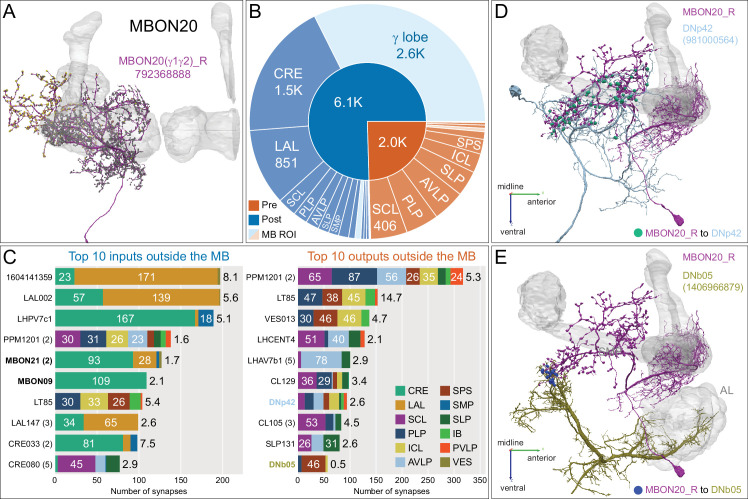
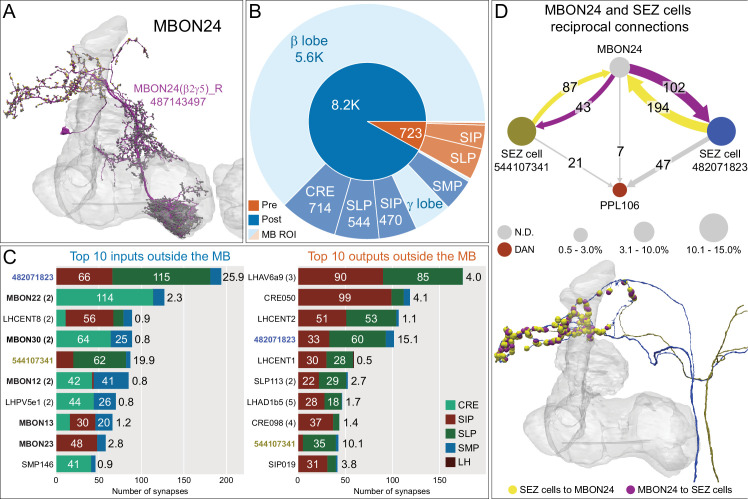
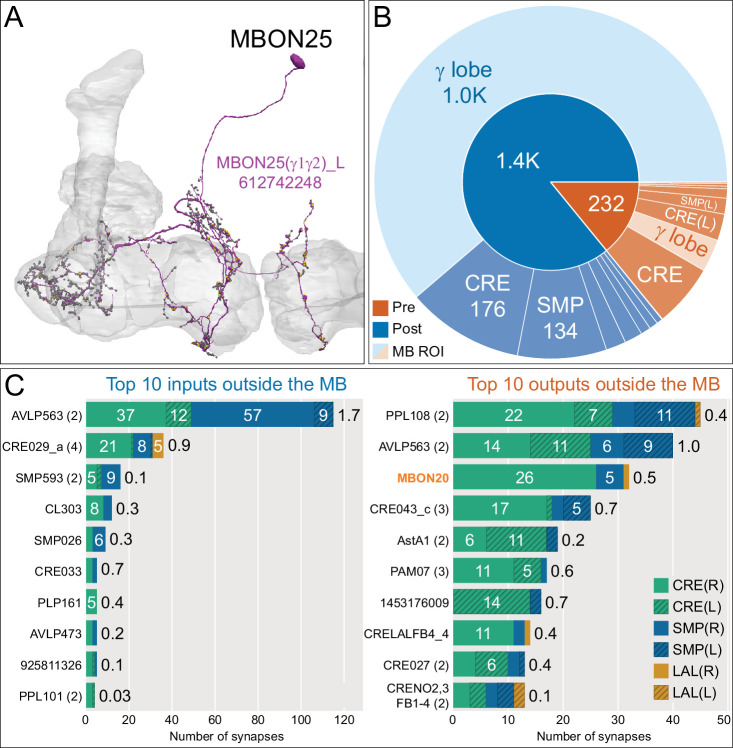
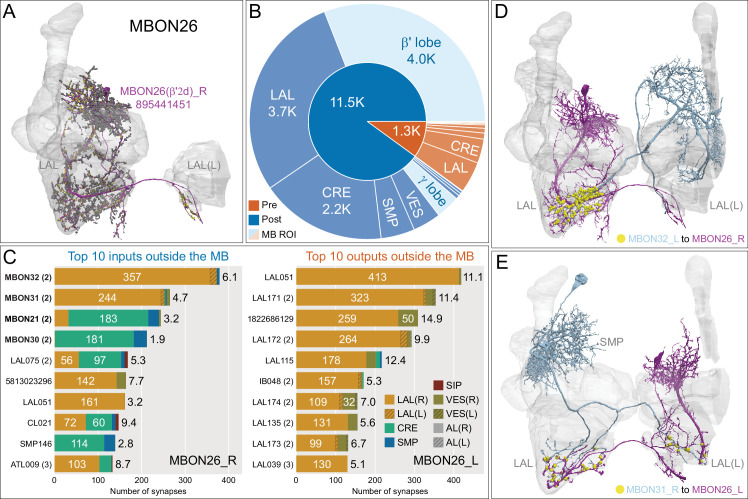
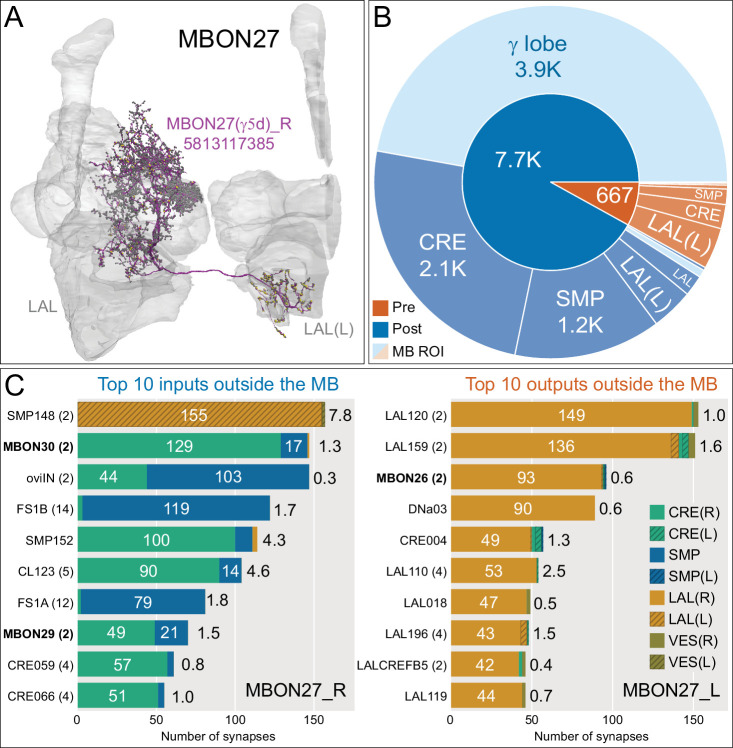
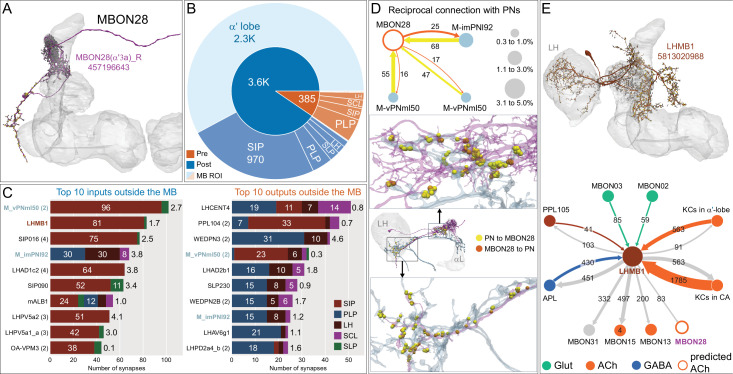
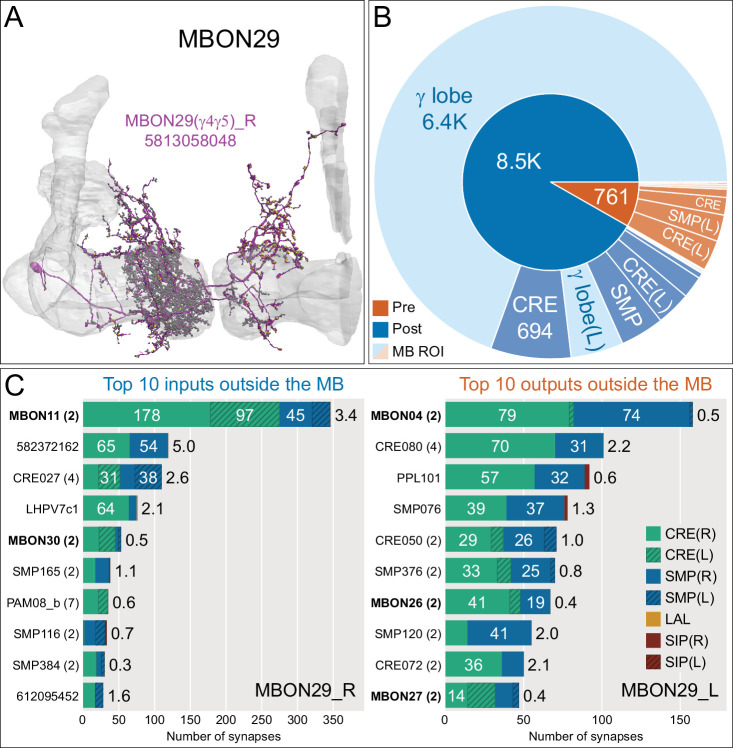
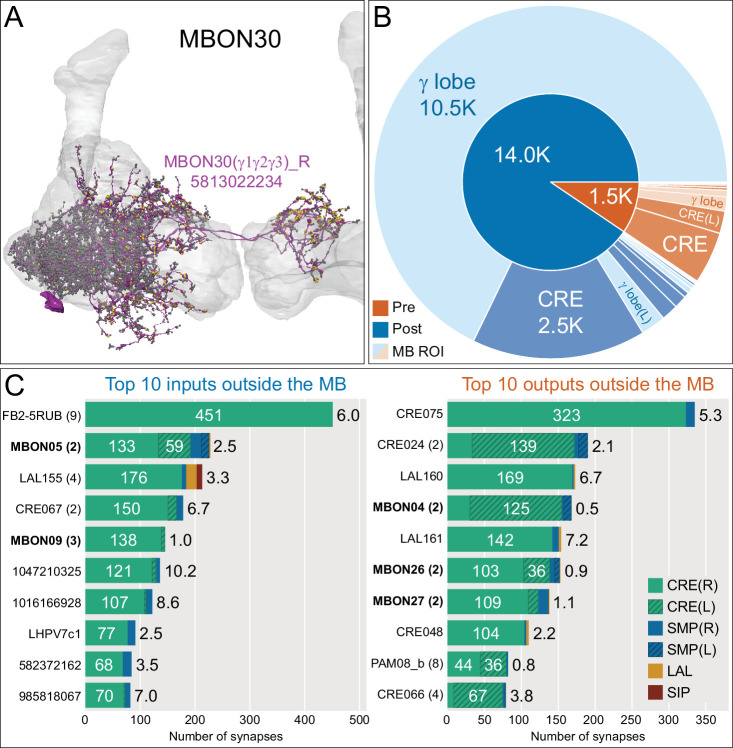
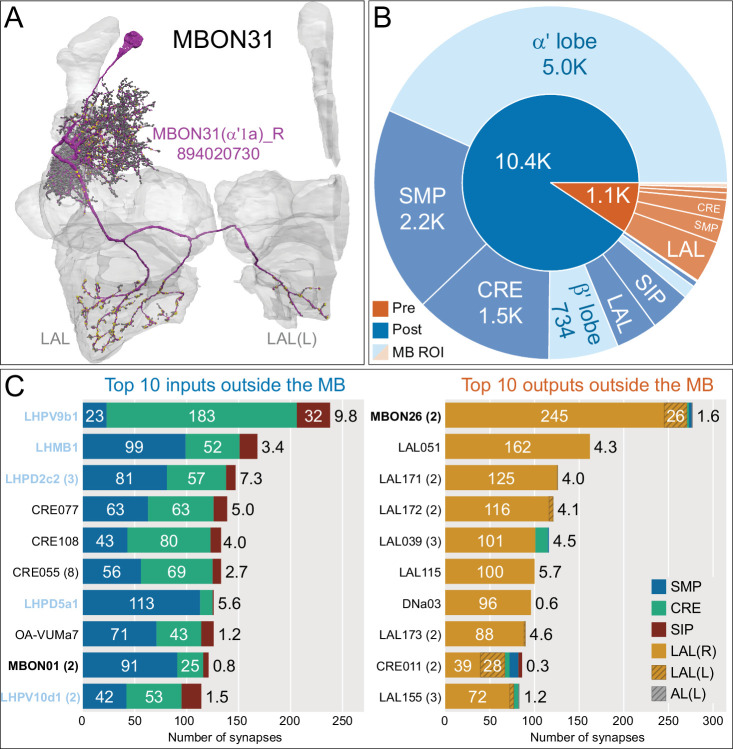
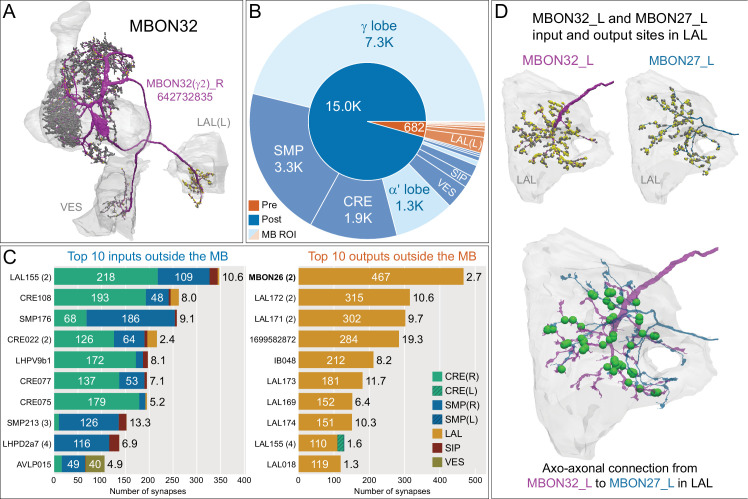
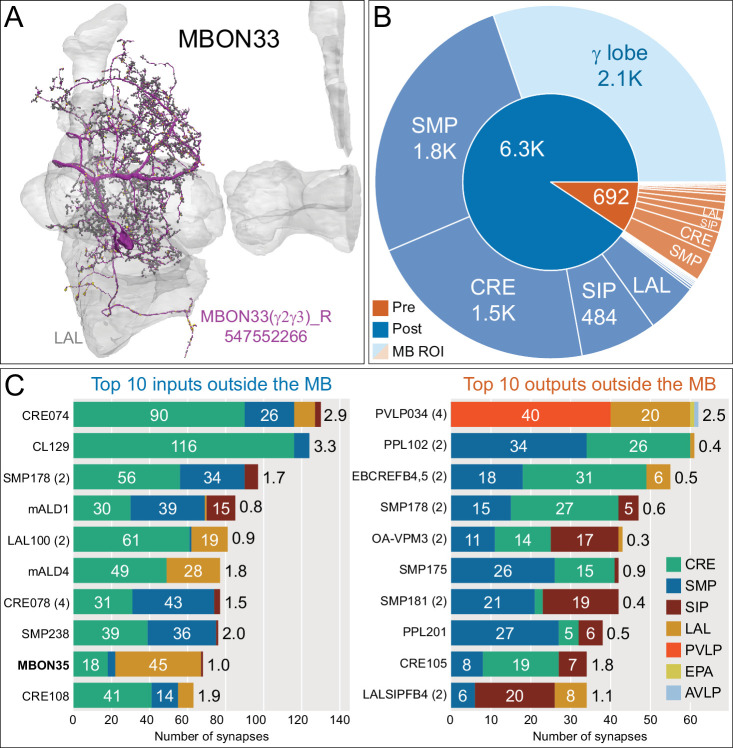
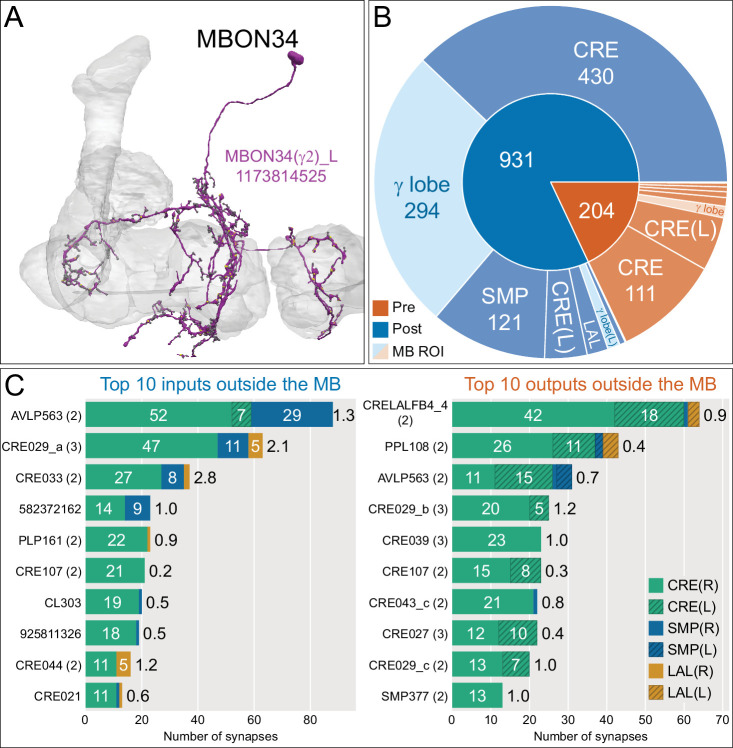
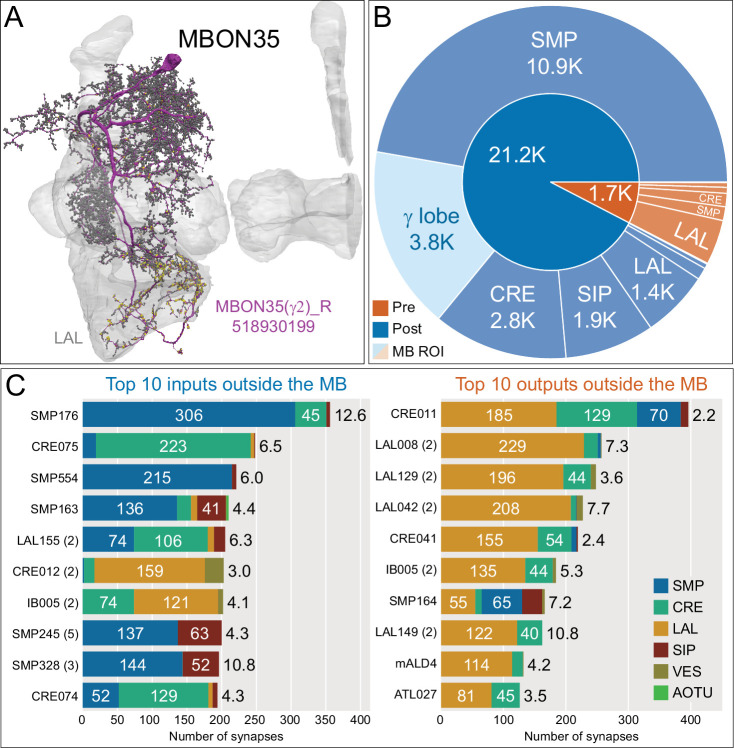
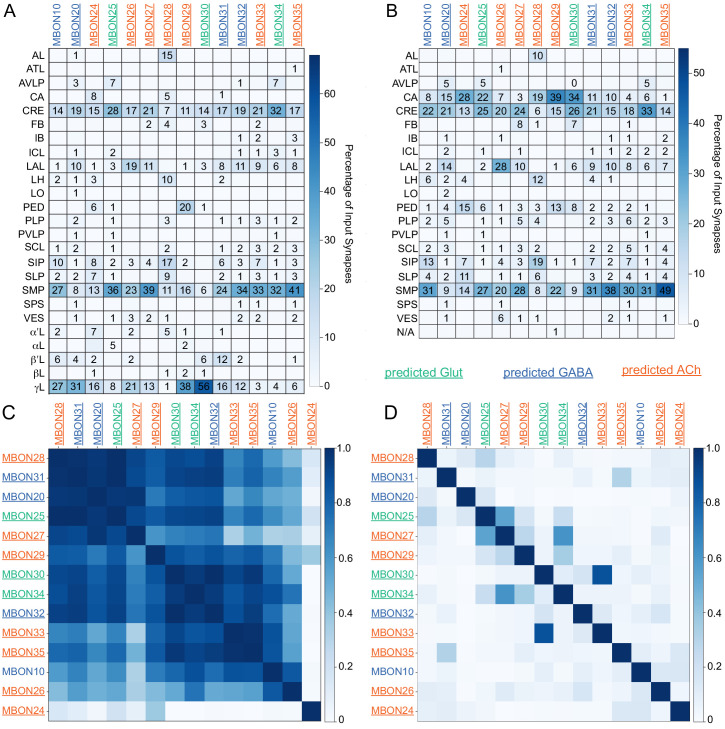
Figure 8. Atypical MBONs.
Each panel shows one of the 14 types of atypical MBONs, with its name, the compartment(s) it innervates and the number of cells of that type per brain hemisphere indicated. Figure 6—figure supplement 1 shows which DANs, MBONs, and KCs are found in each compartment. MB lobes are shown in gray and in the bottom right panel the lateral accessory lobe (LAL) and vest (VES) brain areas are highlighted. Neuronal morphologies are shown with dark gray dots and yellow dots indicating postsynaptic and presynaptic sites, respectively. The MBONs shown in this figure are considered to be atypical in that their dendritic arbors are only partially within the MB lobes. Twelve of these types were discovered in the course of the current study. The other two, the GABAergic MBON10 and MBON20, were described by Aso et al., 2014a, but we have reclassified them here as atypical MBONs because they have dendrites both inside and outside the MB lobes. The three MBON10s in the EM volume have 69 , 68, and 50% of their postsynaptic sites outside the MB lobes; one is shown here. All the other atypical MBONs occur once per hemisphere. Unlike most typical MBONs that innervate brain areas that are dorsal to the MB, six of the atypical MBONs innervate areas that are ventral to the MB. The LAL is a target of several atypical MBONs, and one also innervates the VES. More detailed information about each of the atypical MBONs can be found in Figure 8—figure supplements 1–14 and Figure 8—videos 1–14. Figure 8—figure supplement 15 compares the non-MB inputs to these MBONs. The bounding box for each MBON is color-coded by the neurotransmitter used by that MBON; dashed boxes are used where the transmitter type is based on computational prediction (see Figure 6—figure supplement 2). Links to the neuPrint records of these MBON types are as follows: MBON10, MBON20, MBON24, MBON25, MBON26, MBON27, MBON28, MBON29, MBON30, MBON31, MBON32, MBON33, MBON34, and MBON35.