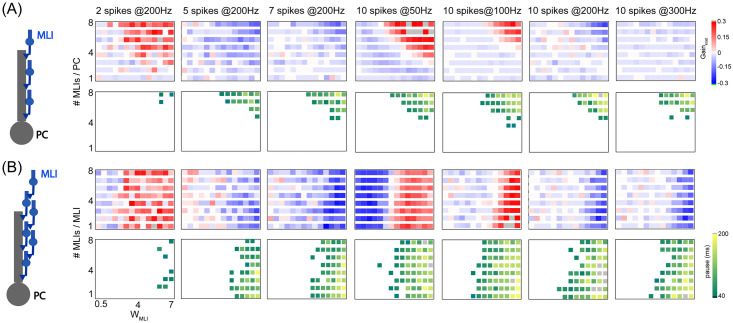
Fig 11. PC synchronization and pause response controlled by MLI inhibition.
(A) PC network with no recurrent MLI inhibition. (Left) Illustration of the PC network receiving different numbers of MLIs. PC synchronization (top) and pause response (bottom) affected by MLI inhibition with stronger weight or more number of MLI-PC synaptic connections per PC, under burst inputs with different spikes and frequencies. Inner rectangles in each panel represent the gain of synchronization under one burst protocol. The gain of synchronization was defined as the relative change of the average Knet. (B) Similar to (A) but for the PC network with recurrent MLIs included, such that each MLI receives 1-8 MLIs recurrently. Here in all plots, each PC receives 8 MLIs.