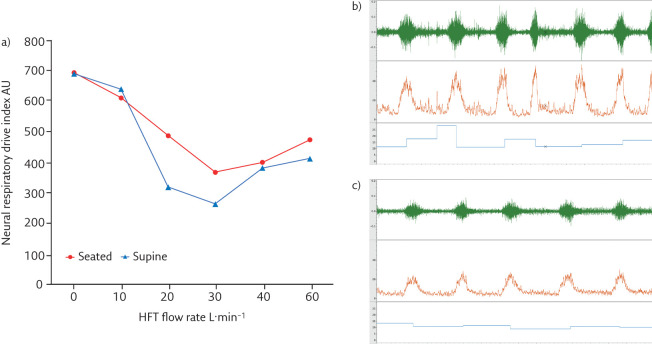
Figure 2.
Changes in neural respiratory drive (quantified using EMGpara) in a patient with stable COPD. a) Neural respiratory drive quantified with EMGpara in a patient with very severe COPD (forced expiratory volume in 1 s <30% predicted). Neural respiratory drive index (the product of normalised EMGpara and respiratory rate, AU=arbitrary units) was measured at baseline and with HFT delivered at 10, 20, 30, 40 and 60 L·min−1 at 37°C, FIO2 0.21. Panels b) and c) illustrate raw EMGpara (mV, green), root mean square EMGpara (µV, orange) and respiratory rate (breaths·min−1, blue). b) High neural respiratory drive observed at baseline. c) Optimal offloading of the respiratory muscle pump observed at 30 L·min−1, with a significant reduction in neural respiratory drive.