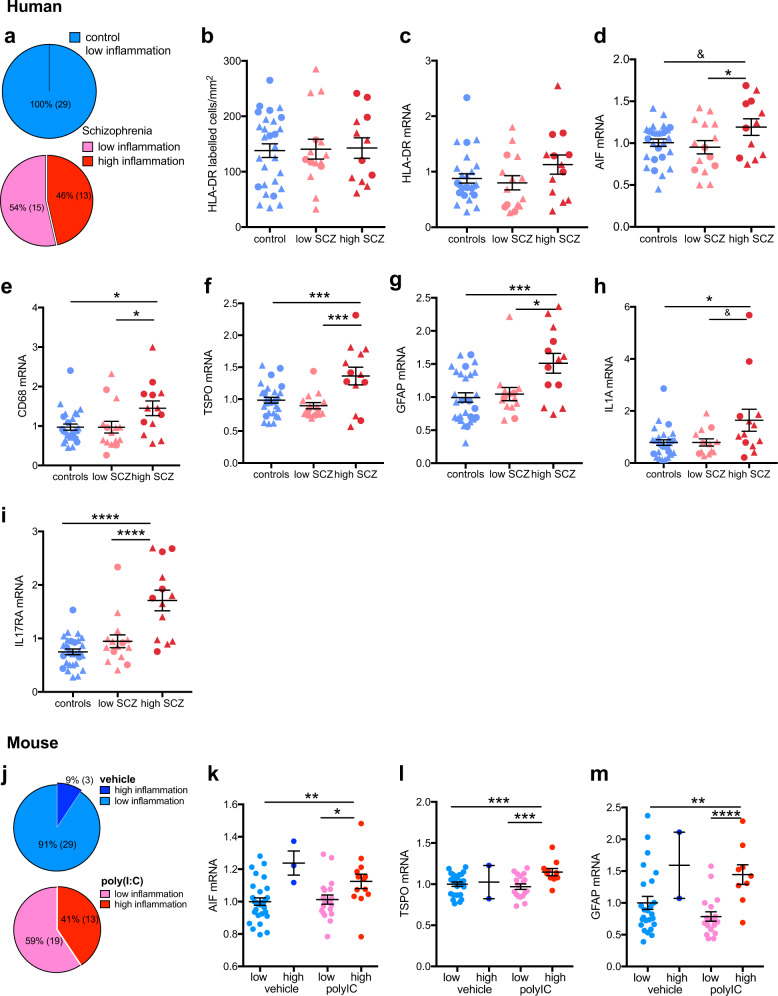
Fig. 3.
Changes in immune-related mRNA expression in midbrain from schizophrenia (SCZ) and control cases and from adult mice prenatally exposed to the viral mimetic, poly(I:C), after stratification into “high” and “low” immune subgroups. a Cluster analysis of immune-related gene expression in midbrain from schizophrenia (SCZ) and control cases revealed that all control cases (blue) and 54% of schizophrenia cases (pink) were of low immune status, whereas 46% of SCZ cases were classified as high immune. b HLA+ microglial cell number and c HLA-DR mRNA did not change in the immune subgroups. d AIF1 mRNA was increased in the SCZ/high immune compared to the SCZ/low immune subgroup. e CD68 and f TSPO mRNAs were increased in the SCZ/high subgroup compared with the SCZ/low and the control groups. g GFAP mRNA was increased in the SCZ/high subgroup compared with the SCZ/low and the control groups. IL1A h and IL17RA i mRNAs were increased in SCZ/high compared with controls and IL17RA mRNA was increased in SCZ/high compared with the SCZ/low subgroup. j Cluster analysis of immune-related gene expression in midbrain from adult mice prenatally exposed to the viral mimetic, poly(I:C) revealed that 91% of vehicle–offspring were of low immune status (light blue) and 9% were of immune status (dark blue). Among poly(IC)-exposed offspring, 59% were classified as low immune (pink), whereas 41% were classified as high immune (red). k AIF1, l TSPO, and m GFAP mRNAs were increased in the poly(IC)/high immune compared with the poly(IC)/low immune and vehicle/low immune subgroups. Data are mean ± SEM. &p < 0.1, *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001