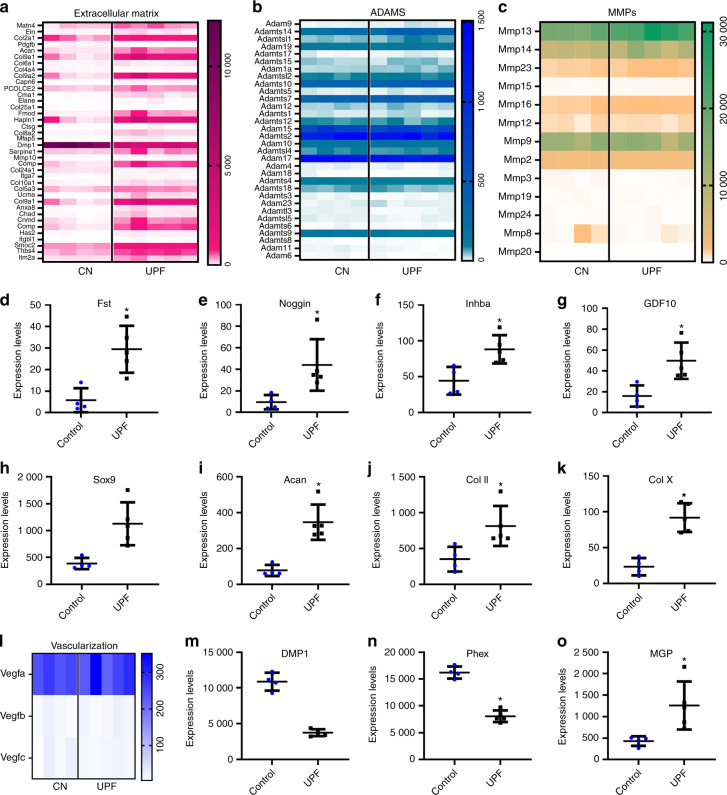
Fig. 4.
Consumption of an ultra-processed diet affects extracellular matrix (ECM) formation and degradation. Heatmaps representing the expression signature of differentially expressed genes in the (a) ECM pathway, (b) A disintegrin and metalloproteinase (ADAM) gene family, and (c) matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) gene family. d–k Expression frequency of genes associated with growth plate (GP) chondrocyte proliferation and differentiation. BPM signaling pathway: d Fst, e Nog, f Inhba and g Gdf10; Sox signaling pathway: h Sox9, i Acan, j Col II and k Col X. l Heatmap representing the expression signature of the VEGF gene family. Expression frequency of genes associated with the mineralization process: m DMP1, n Phex, o MGP. The uniquely mapped reads per gene were counted using HTSeq-count, and differential expression analysis was performed using the DESeq2 R package. * Denotes significant differences from the control group. Genes were considered significantly expressed if the adjusted P value was lower than 0.05. Groups: Control (n = 4) and ultra-processed food (UPF) (n = 5)