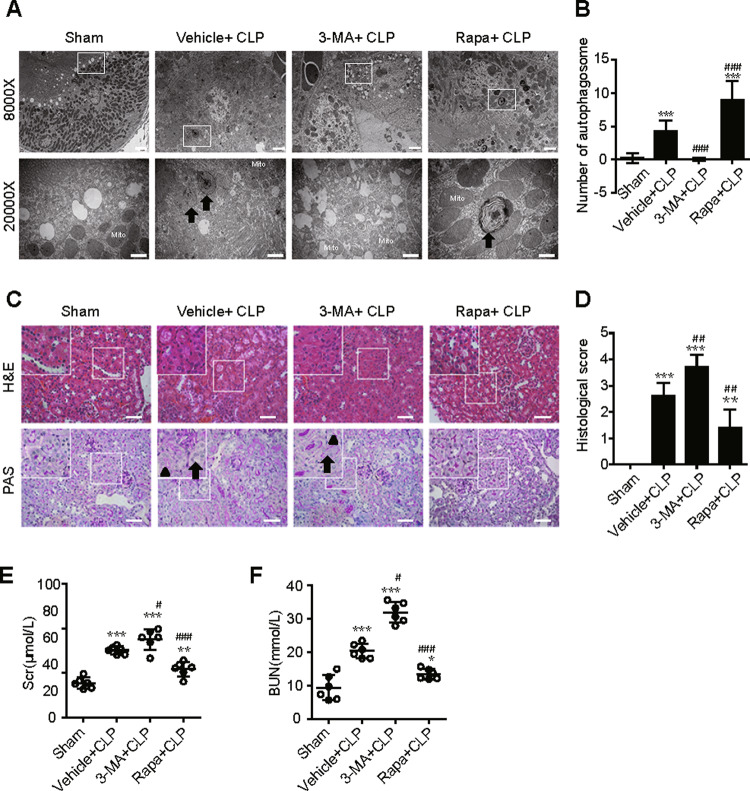
Fig. 2. Activation of autophagy protects against SAKI in RTECs.
Autophagy activation or inhibition by pretreatment with Rapa or 3-MA, respectively. The samples were collected 12 h after CLP-induced SAKI. A, B The number of autophagosomes in renal epithelial cells was calculated in 20 randomly selected fields using a transmission electron microscope (black arrow: autophagosomes; Mito: mitochondrion; upper panel: magnified ×8000 and scale bar = 2 μm; lower panel: magnified ×20000 and scale bar = 1 μm, n = 20). C The irregular brush border (arrow) and ectasia of affected tubules (arrowheads) were observed by H&E staining (upper panel, 200×; inset: 400×; scale bar = 10 μm) and PAS staining (lower panel, 200×; inset: 400×; scale bar = 10 μm) of the kidney cortex. D The tubular damage score was evaluated based on H&E and PAS staining (n = 10). E Scr levels (n = 6). F Serum BUN levels (n = 6). The data are presented as the mean ± SD. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001 vs the sham group; #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01 and ###p < 0.001 vs the vehicle + CLP group. RTECs renal tubular epithelial cells, SAKI sepsis-induced acute kidney injury, CLP caecal ligation and puncture, PAS periodic acid-Schiff staining, H&E haematoxylin–eosin staining, Rapa rapamycin, Scr serum creatinine, BUN urea nitrogen.