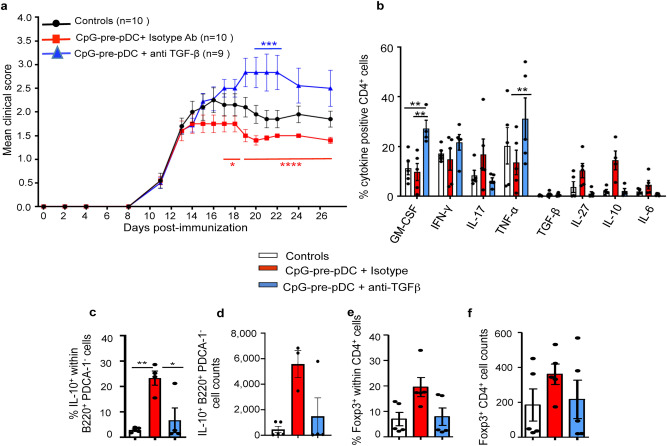
Figure 6.
Role of TGF-β in CpG-pre-pDC mediated protection against EAE. (a) CpG-pre-pDCs were transfected with a neutralizing anti-TGF-β antibody or control isotype antibody using the Chariot protein transfection vector. 80,000 of resulting cells were injected i.v. to MOG35-55 immunized mice at d-12 after immunization. Clinical score (mean ± s.e.m.) was assessed until d-27, n = 10 mice in control and isotype antibody progenitor-treated groups and n = 9 mice in the anti-TGF-β-progenitor-treated group. Statistical analysis was performed using two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post-test: controls vs CpG-prepDC + isotype, d-19, *p = 0.0352; controls vs CpG-prep-DC + anti-TGF-β, d-19, *, p = 0.0144, d20–d22, ***p < 0.0025, d27 *, p = 0.0352; CpG-pre-pDCs + isotype vs CpG-pre-pDCs + anti-TGF-β, d17–18, *, p = 0.0119, d19–d27, ****, p < 0.0001. (b) CD4+ T-cells isolated at d-27 from the spinal cord of controls or recipients of isotype or neutralizing Ab-transfected CpG-pre-pDCs were analyzed by FACS using FMO controls for their cytokine production after 4 h activation with PMA/ionomycin in presence of brefeldin. Mean ± s.e.m. of percentages of cells expressing a given cytokine, n = 5 mice per group. Statistical analysis was performed using two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post-tests, for GM-CSF: Controls vs CpG-pre-pDCs + isotype Ab, NS, Controls vs CpG-pre-pDCs + anti-TGF-β, **, p = 0.0032, CpG-pre-pDCs + isotype vs + anti-TGF-β, **, p = 0.008, *; for TNF-α, CpG-pre-pDCs + isotype vs + anti-TGF-β, **, p = 0.0015. (c, d) Frequency (c) and counts (d) of B220+ PDCA-1− B-cells demonstrating IL-10 production capacity (mean ± s.e.m., n = 5 mice per group, * p = 0.01, **, p = 0.0015, by one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post-tests). (e, f) CD4+Foxp3+ Tregs frequency (e) and cell counts (f), (mean ± s.e.m., n = 5 mice per group), N.S. by analysis using Kruskal–Wallis with Dunn’s post-tests.