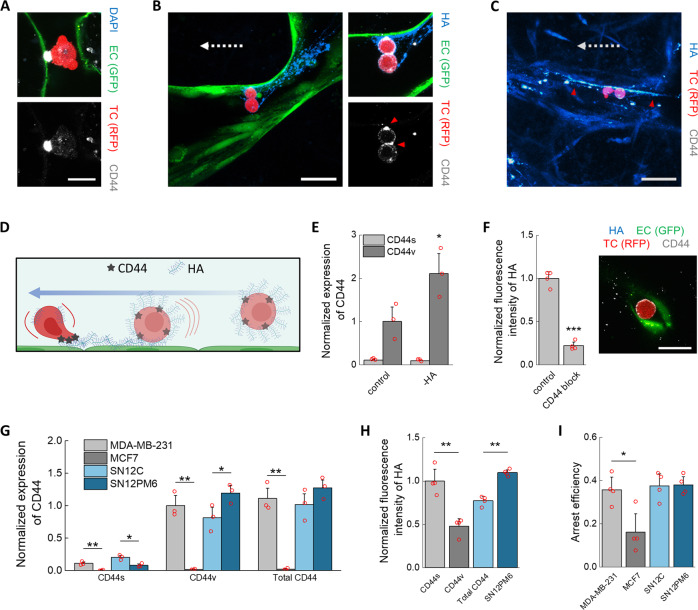
Fig. 4. Mechanisms of arrest and adhesion mediated by the HA–CD44 complex.
A Confocal imaging of arrested TC in the microvasculature and CD44 anchoring. The scale bar is 20 µm. In (B), the TCs are bound through CD44 (red arrows) to streaks of HA. In C, the streaks (red arrows) continue past the TCs, possibly indicating previous deposition. The scale bars for both (B) and (C) are 60 µm. The dashed arrows indicate the direction of flow. D Diagram of GCX-mediated arrest mechanism of TCs, involving deposition of HA upon impact with the endothelium under flow and anchoring to HA through CD44 (partially realized with Biorender.com). E Normalized (to β-actin) expression of CD44 isoforms in TCs after treatment with hyaluronidase in well plates (n = 3 wells). F Expression of HA on TCs after antibody-blocking of CD44 (n = 4 wells) and confocal image of treated TC arrested in a small MVNs capillary, not showing CD44 anchoring or HA. The scale bar is 20 µm. G Normalized (to total protein concentration) expression of CD44 isoforms in various TCs, and H HA expression and I arrest efficiency in the MVNs of the same TCs (n as above, shown for all). Statistical significance was assessed by student’s t test assuming normally distributed data, p < 0.05 *, p < 0.01 **, p < 0.001 ***.