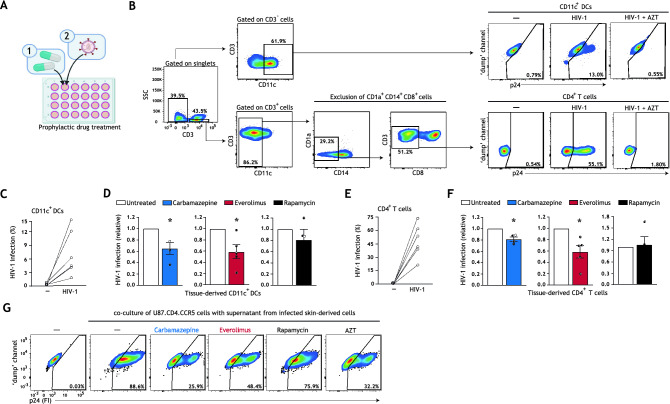
Figure 2.
Prophylactic treatment with autophagy drugs reduces HIV-1 acquisition by tissue-derived DCs and CD4+ T cells. (A) Brief schematic representation of the novel HIV-1 tissue infection model for drug screening; an extended graphical representation of the prophylactic treatment model is available in Figure S3A, Supplementary Information. Biopsies including epithelium and subepithelium were taken from skin and cultured in a 24 well plate. Skin biopsies were prophylactically treated with autophagy drugs and subsequently infected with HIV-1. HIV-1 infection of different cell types and subsets was quantified using multiparameter flow cytometry. (B) Gating strategy utilized to discriminate HIV-1 infection in the emigrated CD11c+ DCs and CD4+ T cells. Treatment of tissue biopsies with HIV-1 replication inhibitor AZT (zidovudine, 20 μM) confirmed productive HIV-1 infection of these cell types. A detailed gating strategy can be found in Figure S4, Supplementary Information. (C–F) Human tissue biopsies were prophylactically treated with carbamazepine (100 μM), everolimus (5 nM), or rapamycin (100 nM) for 15 h, or left untreated, and subsequently infected with HIV-1 NL4.3BaL for 48 h. Emigrated cells were then harvested, washed, and replated for an additional 72 h. HIV-1 infection of emigrated CD11c+DCs was determined as the percentage of CD3−CD11c+p24+ cells (C,D), and HIV-1 infection of emigrated CD4+ T cells as the percentage of CD3+CD11c−CD14−CD1a−CD8−p24+ cells (E,F), determined by flow cytometer. (C–F) Data are mean ± SE of n = 4–5 donors measured in duplicate. Open circles represent the mean of duplicates from each independent experiment. (D,F) Untreated HIV-1 infected cells was set at 1 *P < 0.05; one-sample t test. (G) Skin biopsies including epithelium and subepithelium were prophylactically treated for 15 h with autophagy drugs carbamazepine (100 μM), everolimus (5 nM), rapamycin (100 nM), HIV-1 replication inhibitor AZT (zidovudine, 20 μM), or left untreated, followed by infection with HIV-1 NL4.3BaL. 36 h post-infection, emigrated tissue-derived cells were extensively washed to remove input virus, and replated in new medium in a 96-well plate. Supernatant from infected tissue-derived cells was collected 120 h after replating and co-cultured with U87.CD4.CCR5 cells for 72 h, to further confirm productive HIV-1 infection. A detailed graphical representation of this extracellular virus release assay is available in Figure S3B, Supplementary Information. HIV-1 infection of U87.CD4.CCR5 cells was determined by intracellular p24 staining by flow cytometer. Representative (n = 2 tissue donors) flow cytometry plots of HIV-1 infection of U87.CD4.CCR5 cells incubated with supernatants from HIV-1 infected skin-derived cells is shown.