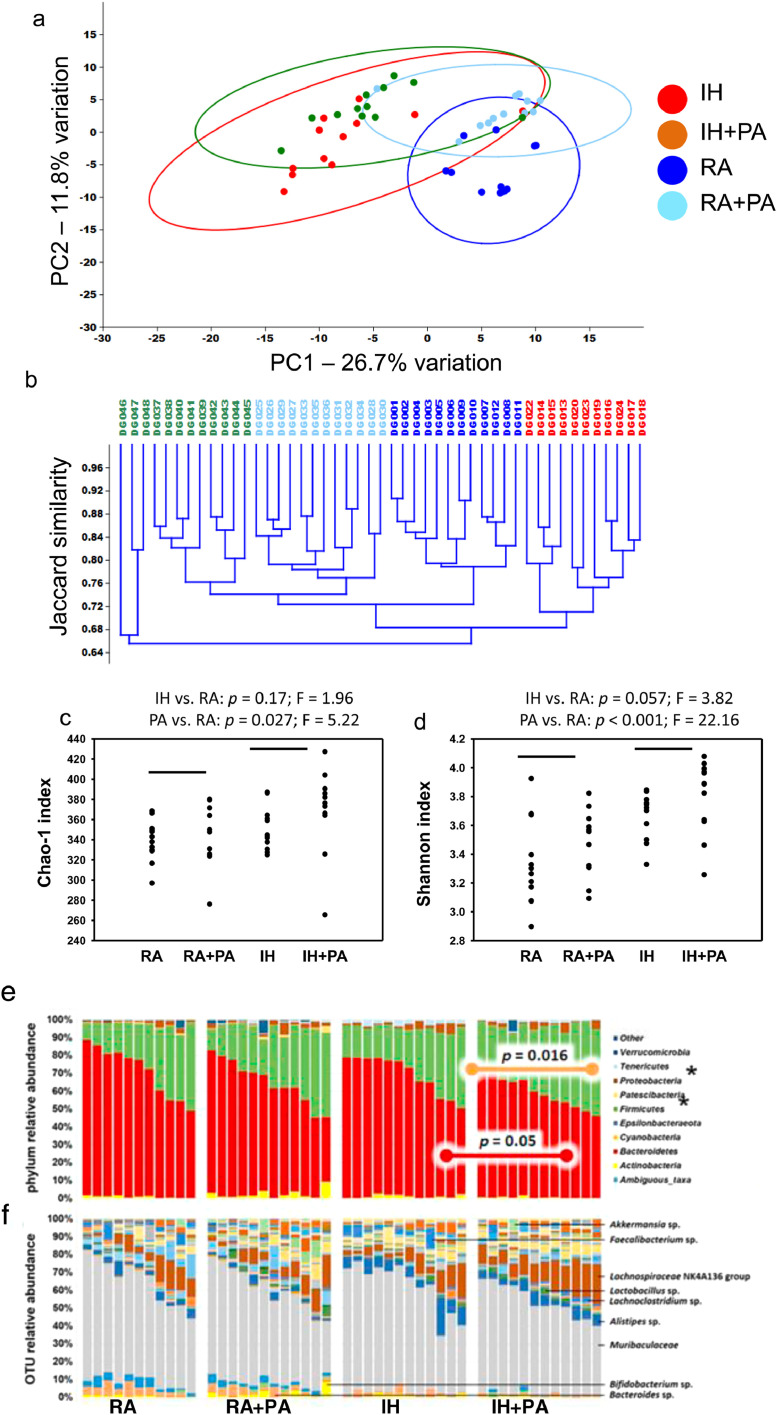
Fig. 3.
Principal component analysis, hierarchical clustering, dot plots and stacked bar charts for 16S RNA analyses of fecal samples obtained from mice exposed to IH, RA for 6 weeks with and without PA. (a) Principal component analysis, and (b) α-diversity in feces of wild-type mice exposed to RA or IH in the presence or absence of PA, p < 0.05 differences between groups (two-way ANOVA with post hoc comparisons using Holm-Sidak method). (c) Stacked bar charts showing the taxonomic distribution of samples within each group at the level of phylum (IH vs. RA: p = 0.17; F = 1.96; PA vs. ctl: p = 0.027; F = 5.22), (d) and operational taxonomic unit with prominent taxa labeled (IH vs. RA: p = 0.057; F = 3.82; PA vs. ctl: p < 0.001; F = 22.16). (e) Principal component analysis, (f) hierarchical clustering according to the unweighted pair group method with arithmetic mean (UPGMA) using Jaccard similarities, to visualize the relationship between the fecal microbiota of mice exposed to different conditions, n = 12/group. Statistical comparisons in PCoA were made using one-way permutational multivariate analysis of variance (PERMANOVA).