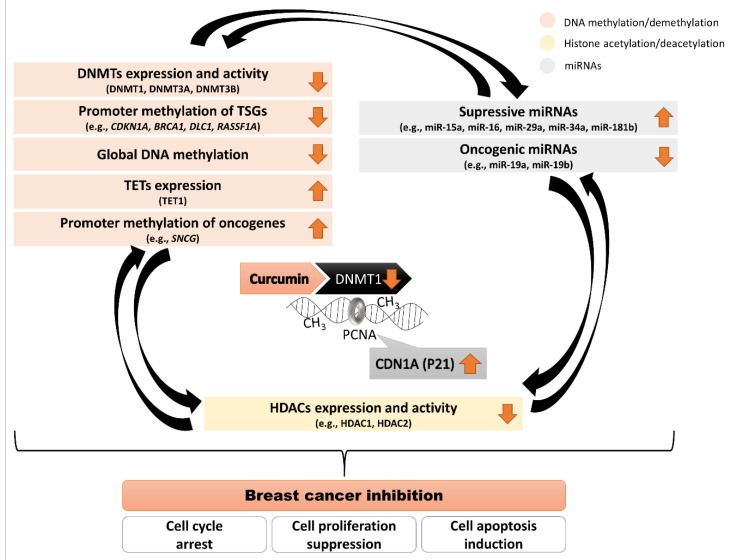
Figure 3.
Scheme demonstrating mechanisms used by curcumin to drive changes in the epigenome in breast cancer inhibition. Curcumin binds to the DNMT1 catalytic domain and impairs its enzymatic activity. PCNA is crucial for DNMT1 activity during replication when DNA methylation pattern is copied from a parental to a daughter DNA strand. CDN1A (P21 encoded by CDKN1A gene) competes with DNMT1 for the same binding site on PCNA, which impairs DNMT1 activity. Curcumin that leads to an increase in P21 expression may affect DNA methylation. Interconnections between the components of the epigenome: DNA methylation, histone modifications and miRNAs. Curcumin driving changes in DNA methylation patterns in breast cancer cells may have indirect effects on other epigenetic components (histone modifications and miRNAs) and vice versa.