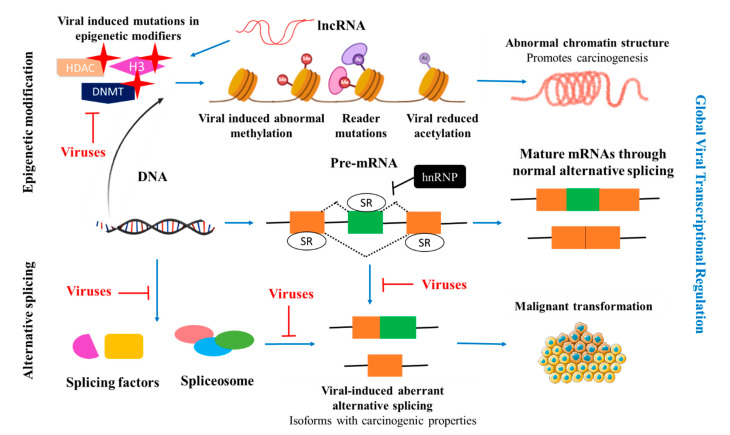
Figure 1.
Global virally-induced transcriptional regulation. Viral infections hijack cellular splicing machinery and enhanced epigenetic modifications to promote carcinogenesis through abnormal methylation caused by genetic alterations, histone modification and DNA methylation. Moreover, viral proteins repress the expression and inhibit the binding of splicing factors to modulate aberrant splicing, thereby producing mRNA isoforms with carcinogenic properties that drive cellular transformation [20,26]. hnRNP: heterogeneous ribonucleoproteins; lncRNA: long non-coding RNA; HDCA: Histone deacetylases; DNMT: DNA methyltransferase; H3: Histone H3.