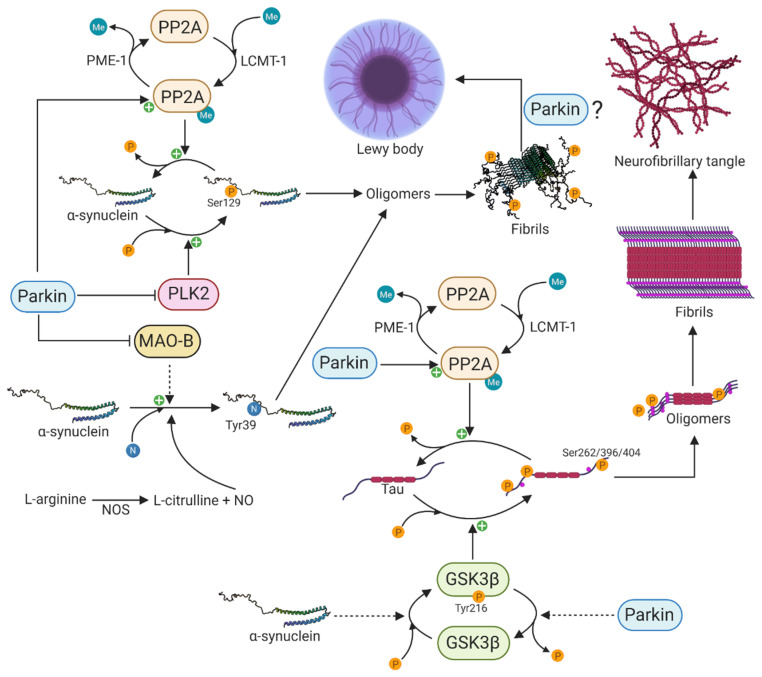
Figure 3.
Functional interaction between α-synuclein and parkin in protein aggregation. Parkin can prevent protein aggregation and neurofibrillary tangles through its activation of PP2A. PP2A is able to dephosphorylate both pSer262/396/404 tau and pSer129 α-synuclein, thereby attenuating the formation of toxic oligomers and eventually Lewy bodies and neurofibrillary tangles. Parkin is also able to inhibit the activity of PLK2 that normally phosphorylates α-synuclein on serine 129. Inhibition of MAO-B by parkin results in decreased oxidative stress and decreased formation of Tyr39 nitrated α-synuclein and oligomer formation. Parkin and α-synuclein have opposite functions regarding the activity of the major kinase GSK3β that phosphorylates tau. The phosphorylation of GSK3β at Tyr216 is dependent on α-synuclein, whereas its dephosphorylation is indirectly regulated by parkin. Created with BioRender.com.