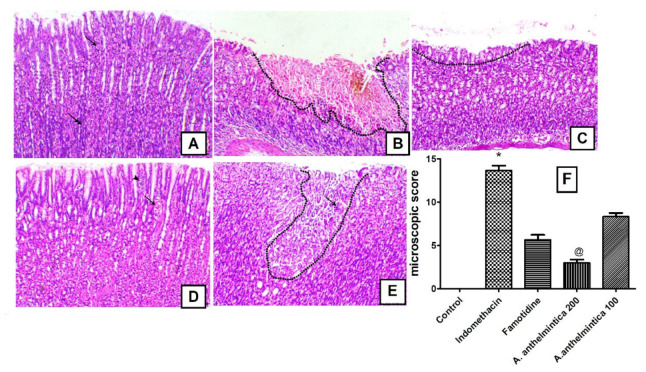
Figure 3.
A photomicrograph of histopathological changes: (A) Control with normal gastric mucosa (arrow indicates normal parietal cells and double arrow indicates normal surface mucous cells); (B) indomethacin group showing severe degree of coagulative necrotic changes within the gastric mucosa (area above the dotted line) accompanied with deposition of acid hematin (arrow) and inflammatory cell infiltration (arrowheads); (C) famotidine-treated group showing marked decreases in the degenerative and necrotic changes within the gastric mucosa (area above the dotted line); (D) A. anthelmintica extract (200 mg/kg)-treated group showing a marked decrease in the degenerative changes within gastric glands (arrow indicates mild congestion of the gastric capillaries) and few lymphocytes within the surface mucosal lining (arrowhead); (E) A. anthelmintica extract (100 mg/kg)-treated group showing foci of degenerative gastric mucosa (area above the dotted line) revealing few necrotic gastric glands (arrow)), H&E, 100×, bar = 100 µm. (F) Microscopic scores in gastric tissues of rats of different experimental groups. Values are mean ± SEM from 6 samples using Kruskal–Wallis followed by Dunn’s post hoc test. * p < 0.05, compared with control; @ p < 0.05, compared with indomethacin.