Figure 2.
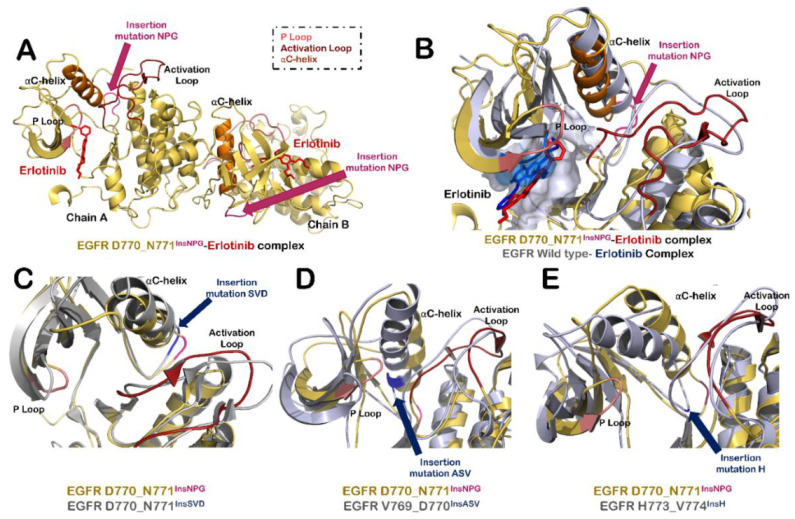
Structural modifications in EGFR protein due to insertion mutations in exon 20. (A) Structure of EGFR dimer having D770_N771InsNPG mutation in complex with erlotinib. Insertion mutation is highlighted in pink color. Other highlighted structural elements around ATP binding site of protein include activation loop (shown in firebrick red color), α-C helix (orange) and P loop (salmon). (B) Superimposed structure of ATP binding site of Chain A of wildtype EGFR- erlotinib complex (grey-blue) with that of EGFR D770_N771InsNPG–erlotinib complex (yellow-red). (C) Superimposed structure of ATP binding site of Chain A of EGFR D770_N771InsNPG (yellow-red) mutant with that of EGFR D770_N771InsSVD (grey-blue). (D) Superimposition of ATP binding site of Chain A of EGFR D770_N771InsNPG (yellow-red) with EGFR V769_D770InsASV (grey-blue). (E) Superimposed structure of ATP binding site of Chain A of EGFR D770_N771InsNPG (yellow-red) with that of EGFR H773_V774InsH (grey-blue).
