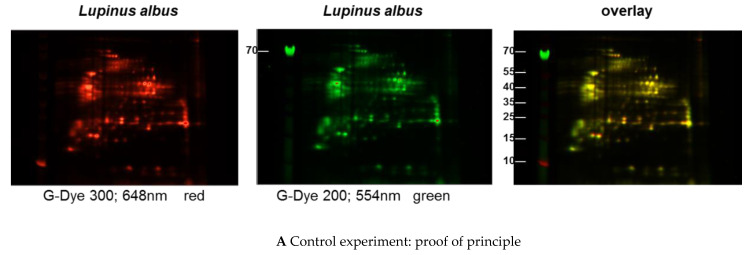
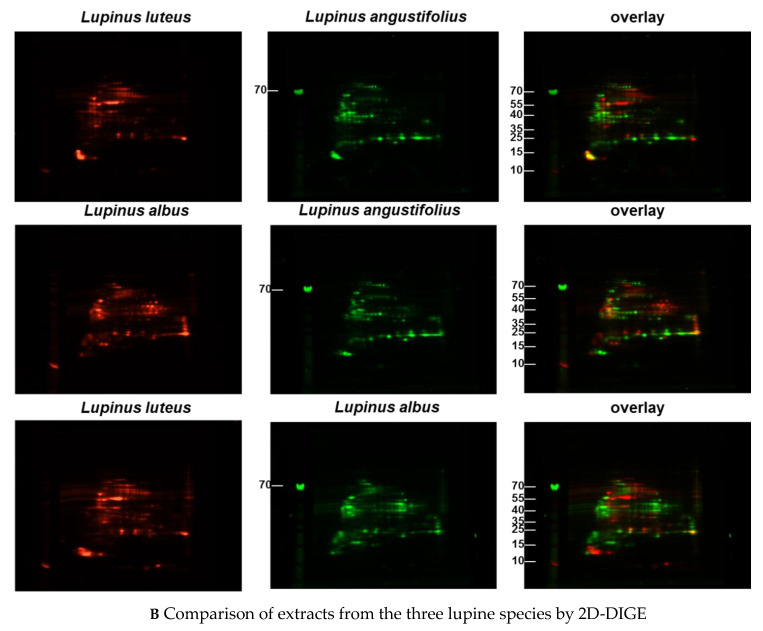
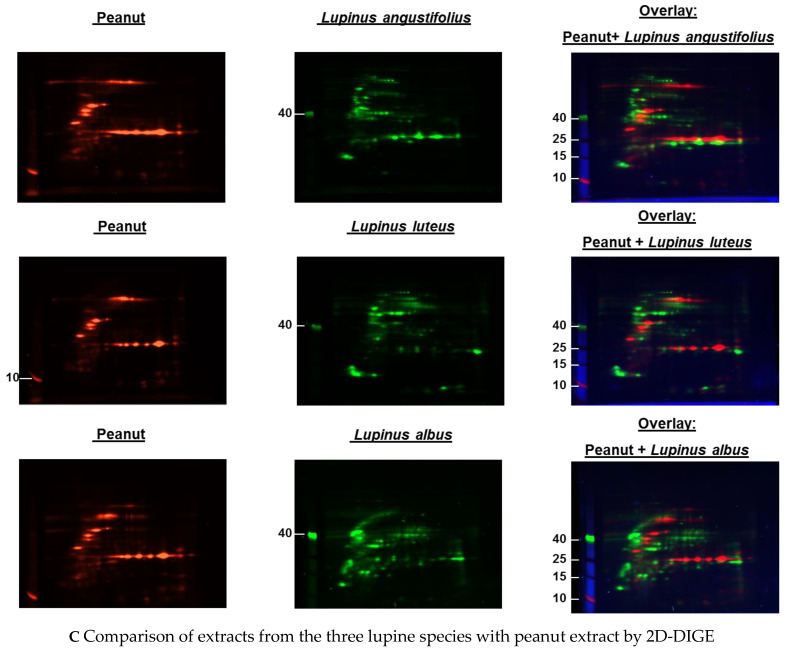
Figure 1.
(A–C) Protein extracts obtained via alkaline extraction of flour from all three lupine species were studied by 2D-DIGE. (A) The control experiment shows the complete identity of the differently dyed samples of an alkaline extract of Lupinus albus by turning to yellow after having overlaid the two complementary colors, red and green. (B) By comparison of extracts from the three lupine species by 2D fluorescence difference gel electrophoresis (2D-DIGE), it becomes evident that there is no strong identity. On the contrary, the dominance of the single colors in the overlay speaks in favor of a broad molecular diversity of the dyed proteins in the different extracts. Whether the diversity is mirrored by immunological diversity was part of the subsequent investigations. (C) When comparing peanut extract with the extracts from different lupine species, there are only a few yellow areas. In addition, the differences between the lupine species become evident in this experiment as well, as there are different distributions of proteins colored green (lupine) when overlaid with peanut proteins dyed red.