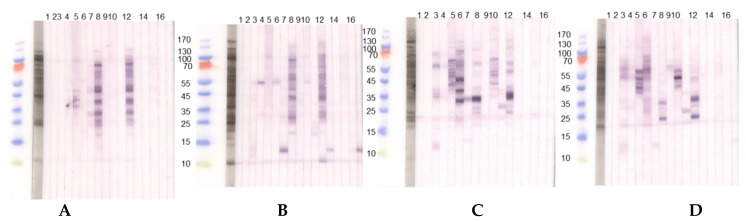
Figure 2.
Immunoblots with acidic extracts (0.1 M CH3COONH4, pH 5.0), TTBS blocking and dilution of sera 1:10 with two different lupine species, (A) L. angustifolius and (B) L. luteus chosen as examples. (1) Tris control; (2) negative control serum; (3) lupine and peanut allergy (P 6); (4) legume allergy, suspected lupine allergy, lupine-sensitized (P 2); (5) peanut allergy, suspected lupine allergy, lupine-sensitized (P 3); (6) lupine allergy (P 23); (7) lupine allergy (P 10); (8) peanut allergy, lupine-sensitized (P 24); (9) lupine and peanut allergy (P 25); (10) lupine and peanut allergy (P 26); (11) peanut allergy, suspected lupine allergy (P 27); (12) peanut allergy, lupine-sensitized (P 4); (13) peanut allergy, lupine-sensitized (P 13); (14) lupine allergy (P 29); (15) peanut allergy and suspected lupine allergy (P 28); (16) suspected lupine allergy, lupine-sensitized (P 14); (17) peanut allergy, lupine-sensitized (P 12). (C,D) Immunoblots with alkaline extracts (0.2 M NH4HCO3, pH 8.0) of (C) L. angustifolius and (D) L. luteus with sera from the same patients. For sera from some individuals (P 4, P 10, P 12, P 13, P 14) differences regarding the IgE-reactivity to different lupine species are detectable. Particularly, sera from P 10, P 12, and P 13 showed reactivity to one LMW protein in the L. luteus extract, which we decided to work upon further since the reactivity was dominant when compared to weak or missing reactivity to other proteins in the extract. (P-code corresponds with Table 1.).