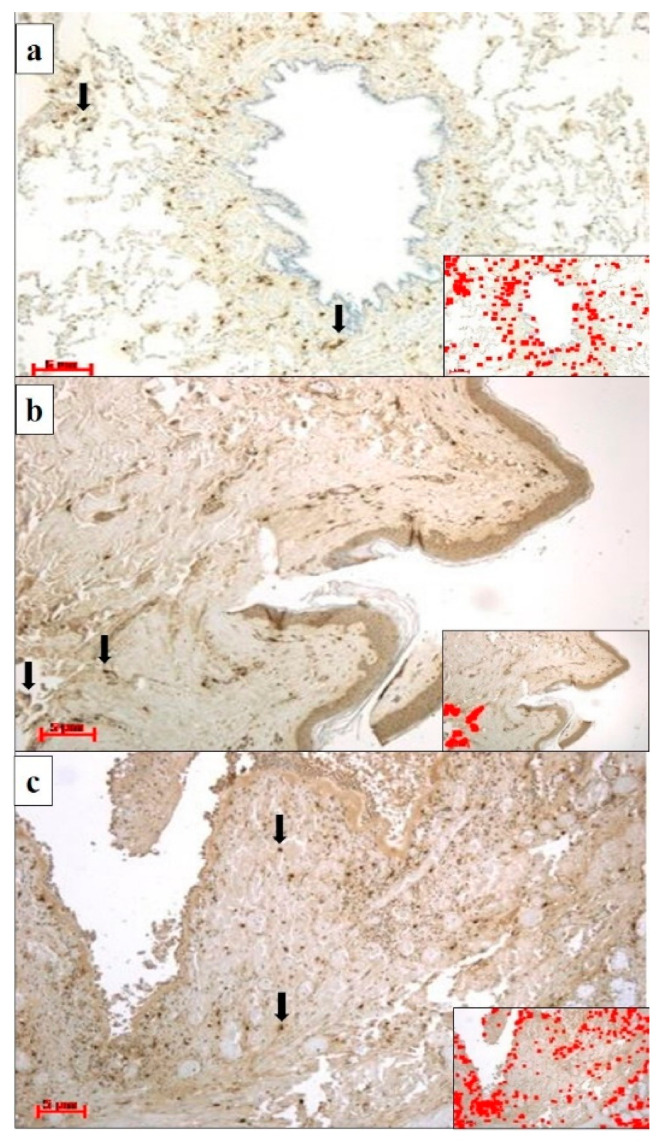
Figure 1.
(a) Lung specimens from a cadaver who had died of anaphylactic shock; anti-tryptase antibody staining is strongly expressed in mast cells (black arrows) in the peribronchial interstitium. The insert shows the immunostaining software image analysis of Figure 1a, in which a highly immunostained area (red color) was detected (magnification: 20×; scale bar: 5 µm). (b) Skin specimens of the gluteus where medication administration occurred from a cadaver who had died of anaphylactic shock; anti-tryptase immunolocalization (black arrows) was demonstrated in the derma of the medication injection site. The insert shows the immunostaining software image analysis of Figure 1b, in which a highly immunostained area (red color) was detected (magnification: 20×; scale bar: 5 µm). (c) Glottis specimens of a cadaver who had died of anaphylactic shock showed strong anti-tryptase immunoexpression in mast cells (black arrows). The insert shows the immunostaining software image analysis of Figure 1c, in which a highly immunostained area (red color) was detected (magnification: 20×; scale bar: 5 µm).