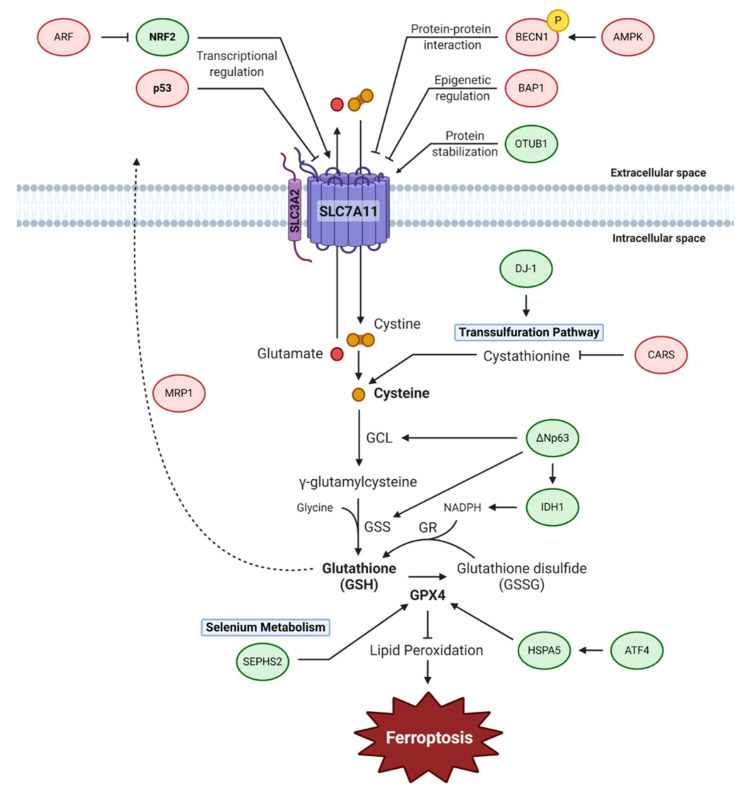
Figure 2.
The cyst(e)ine-glutathione-GPX4 axis regulates ferroptosis. The cystine/glutamate antiporter, system Xc−, is composed of two subunits, SLC7A11 and SLC3A2. System Xc− is the dominant pathway for regulating cysteine levels within cells by transporting cystine into cells. An alternate pathway for synthesizing cysteine is through the transsulfuration pathway. Cysteine is used as a substrate for glutathione biosynthesis, which is further used to activate GPX4 to inhibit lipid peroxidation. This antioxidative activity of GPX4 allows for the prevention of ferroptosis. Selenium metabolism is important for the activity of GPX4, which is a selenoprotein. Ferroptosis inhibiting and inducing factors are indicated in green and red, respectively. (Abbreviations: AMPK, AMP-activated protein kinase; ARF, alternative reading frame; ATF4, activating transcription factor 4; BAP1, BRCA1-associated protein 1; BECN1, beclin 1; CARS, cysteinyl-tRNA synthetase; DJ-1/PARK7, cancer- and Parkinson’s disease (PD)-associated protein; GCL, glutamate-cysteine ligase; GPX4, glutathione peroxidase 4; GR, glutathione reductase; GSS, glutathione synthetase; HSPA5, heat shock protein family A member 5; IDH1, isocitrate dehydrogenase 1; NADPH, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate; ΔNp63, N-terminal truncated isoform of p63; NRF2, nuclear factor erythroid 2–related factor 2; OTUB1, OTU deubiquitinase, ubiquitin aldehyde binding 1; SEPHS2, selenophosphate synthetase 2; SLC3A2, solute carrier family 3 member 2; SLC7A11, solute carrier family 7 member 11).