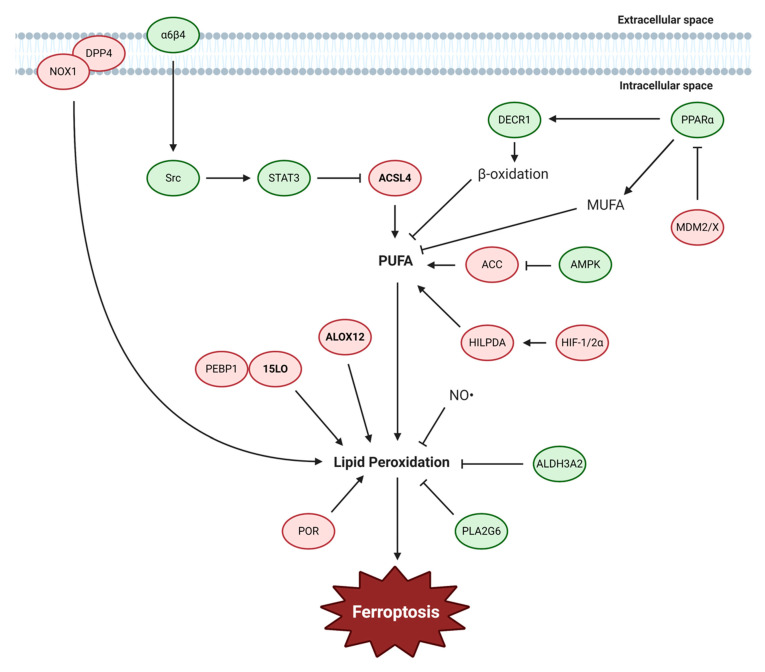
Figure 3.
Lipid metabolism regulates ferroptosis. The major stages of lipid metabolism that regulate ferroptosis are the generation of PUFA and the induction of lipid peroxidation. ACSL4 is the major enzyme that generates PUFAs which drive ferroptosis. In the case of lipid peroxidation, ALOX and other factors can contribute to the production of lipid peroxides. Ferroptosis inhibiting and inducing factors are indicated in green and red, respectively. (Abbreviations: 15LO, 15-lipoxygenase; ACC, acetyl-CoA carboxylase; ACSL4, acyl-CoA synthetase long-chain family member 4; ALDH3A2, aldehyde dehydrogenase 3 family member A2; ALOX, arachidonate 5-lipoxygenase; AMPK, 5′ AMP-activated protein kinase; DECR1, 2,4-dienoyl-CoA reductase 1; DPP4, dipeptidyl-peptidase 4; HIF-1/2α, hypoxia-inducible factor 1/2α; HILPDA, hypoxia inducible lipid droplet associated; MDM2/X, murine double minute family members 2/X; MUFA, monounsaturated fatty acids; NO, nitrogen oxide; NOX1, NADPH oxidase 1; PEBP1, phosphatidylethanolamine binding protein 1; PLA2G6, phospholipase A2 group VI; POR, P450 oxidoreductase; PPARα, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha; PUFA, polyunsaturated fatty acids; STAT3, signal transducer and activator of transcription 3).