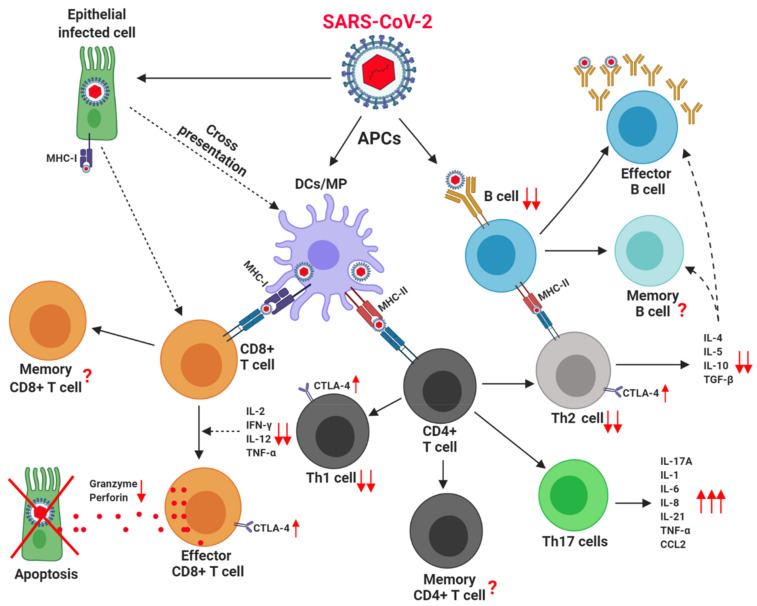
Figure 3.
Adaptive Immune cells in obese/T2D patients, with critical COVID-19. Obese and T2D patients have pre-existing adaptive immune cell alterations. SARS-CoV-2 can infect antigen-presenting cells (APC) such as DCs, MP, and B cells, which present viral antigens to T cells via MHC I and MHC-II molecules. MHC-I molecules present cytoplasmic viral protein to CD8+ T cells; while MHC-II molecules present endoplasmic viral proteins to CD4+ T cells. Additionally, SARS-CoV-2 can directly infect other cells (e.g., epithelial cells), which could depend on cross-presentation of viral antigens by DC to activate virus-specific CD8+ T cells. Lymphocytopenia is a hallmark feature of severe COVID-19. The release of cytokines by CD4+ Th1 and Th2 cells appears to be decreased. In contrast, the expression of inhibitory molecule CTLA-4 appears to increase. The frequency and function of Th17 cells appears to predispose the development of ARDS. Despite the low number of B-lymphocytes IgG and IgA specific antibodies seems to be high. APC: Antigen presenting cells, IL: interleukins, TNF: Tumor necrosis factor, IFN: Interferon, DC: Dendritic cells, MP: Macrophages, MHC: Major histocompatibility complex, CTLA-4: Cytotoxic T-Lymphocyte Antigen 4, Th: T helper cells, CCL2: Chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 2. Created with BioRender.com.