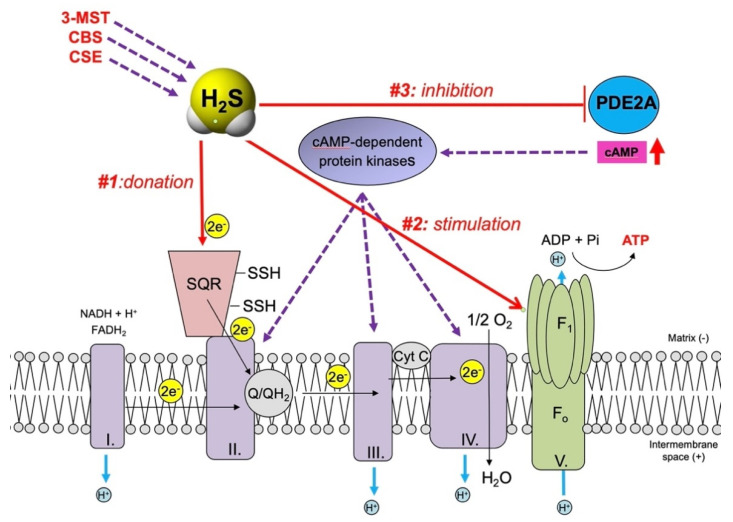
Figure 1.
Mechanisms by which mitochondrial H2S (produced by CBS, CSE or 3-MST) can stimulate mitochondrial electron transport and aerobic ATP generation in cancer cells. #1: H2S acts as a direct electron donor at the level of SQR, which feeds electrons into the electron transport chain at the level of Complex II. #2: H2S inhibits intramitochondrial cAMP phosphodiesterase; this results in an elevation of intramitochondrial cAMP, which, in turn, phosphorylates electron transport chain proteins via the activation of intramitochondrial cAMP-dependent protein kinases. #3: H2S acts as direct stimulator of ATP synthase activity via sulfhydration of the α subunit (ATP5A1) at Cys 244 and Cys 294.