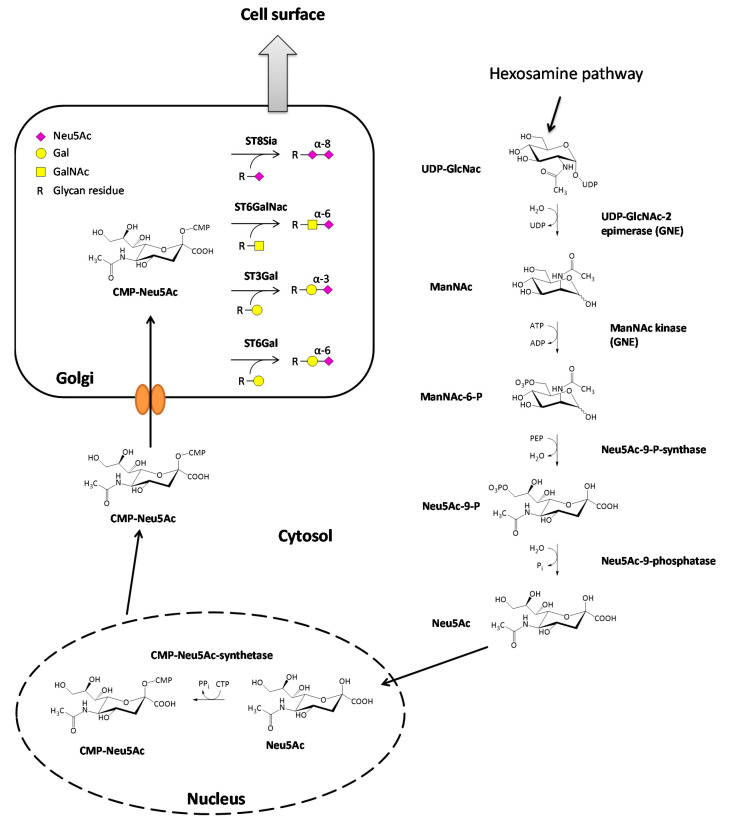
Figure 1.
Biosynthesis of sialic acids and attachment to glycan structures. The most common sialic acid in humans is N-Acetylneuraminic acid (Neu5Ac), which is derived from uridine diphosphate-N-acetylglucosamine (UDP-GlcNAc) in the cytosol. In the nucleus, Neu5Ac reacts further with cytidine triphosphate CTP, and the activated form cytidine monophosphate(CMP)-Neu5Ac is synthesized. CMP-Neu5Ac is then transported to the Golgi apparatus where four groups of sialyltransferases (ST8Sia, ST6GalNAc, ST3Gal, ST6Gal) exist, which attach Neu5Ac to glycan residues of glycolipids or glycoproteins. Afterward, the modified molecules are transported to the cell surface.