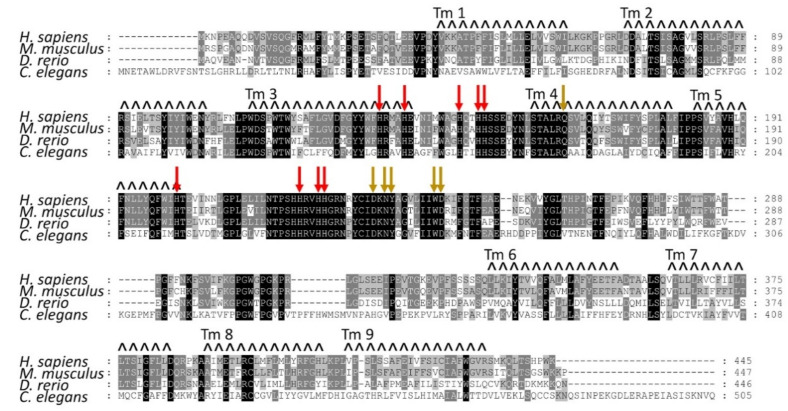
Figure 2.
Sequence alignment of Homo sapiens, Mus musculus, Danio rerio, and Caenorhabditis elegans Agmo and AGMO topology. Red arrows indicate the nine conserved histidines at positions 132, 136, 145, 148, 149, 201, 221, 224, and 225 of the human AGMO, which shape the catalytic centre. Beige arrows show six additional residues that are all essential for AGMO activity and conserved across all species (Q162, D233, N235, Y236, W243 and D244 in the human AGMO sequence). The nine transmembrane domains (Tm) are marked with staggered lines (Tm 1, 40–61; Tm 2, 70–104; Tm 3, 111–137; Tm 4, 157–179; Tm 5, 183–201; Tm 6, 334–354; Tm 7, 363–383; Tm 8, 390–409; and Tm 9, 413–433 of the human AGMO sequence). Accession numbers for all species are as follows: NP_001004320.1 (H. sapiens), NP_848882.2 (M. musculus), NP_998048.2 (D. rerio), and NP_499664.2 (C. elegans). Program alignment of protein sequences was done by ClustalW incorporated into the MEGA-X package using default parameters and visualised by Genedoc (shading of similarity groups disabled).