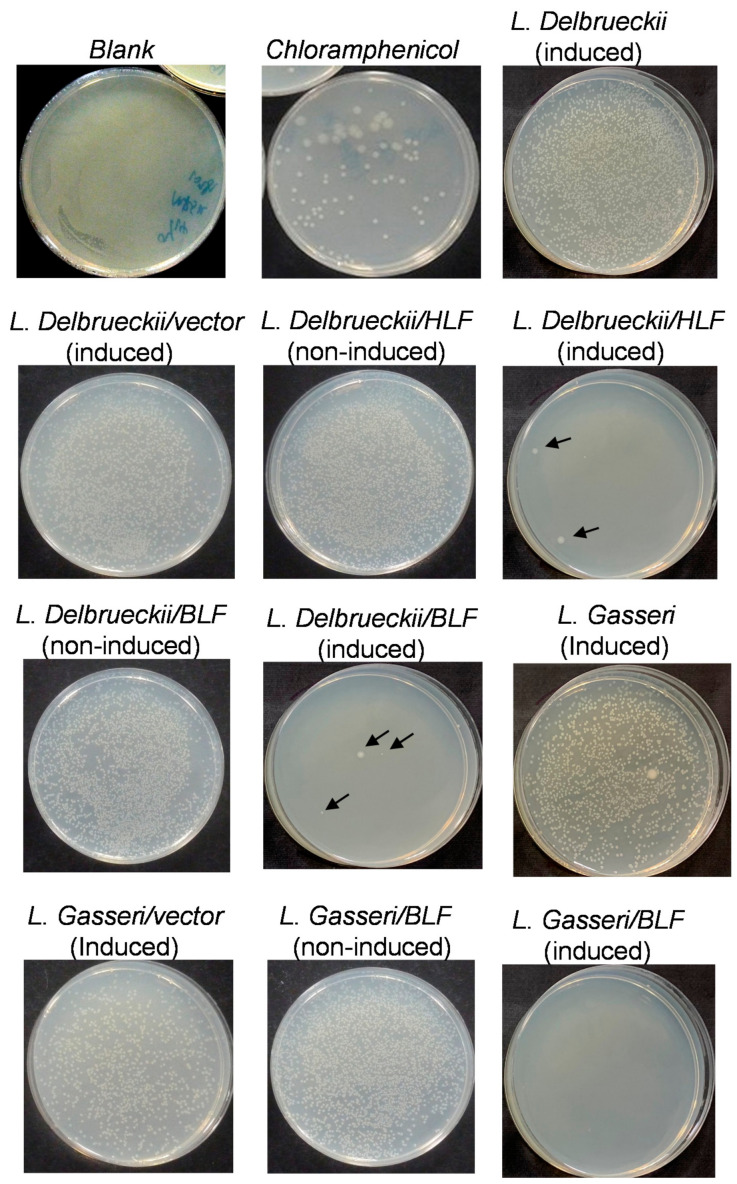
Figure 7.
Effects of recombinant human or bovine lactoferrin cell lysates on the growth of Staphylococcus aureus. About 100 mL L. delbrueckii (host control), L. delbrueckii/pNZ8148 (vector control), L. delbrueckii/HLF, L. delbrueckii/BLF, L. gasseri (host control), L. gasseri/pNZ8148 (vector control), and L. gasseri/BLF was induced by protein expression for 5 h using nisin. Cell pellets were harvested, washed by phosphate-buffered saline twice, and then disrupted by sonication. Supernatants (cell lysates) were then harvested by centrifugation. Supernatants (200 μL/assay) were mixed with pathogenic bacterial broth (1 × 104 cfu/mL; 300 μL) in Eppendorf, and these mixers were further incubated for 24 h at 37 °C. Then, 200 μL of the mixtures was further plated onto nutrient agar (NA) plates to reveal the remaining growth of bacterial colonies. Arrows indicate the grown of individual bacterial colonies. The final concentration of 12.5 μg/mL chloramphenicol was also used as the control. The blank control presented as smear-type bacterial, revealing countless pathogenic bacterial colonies grown on the NA plates, and the induced L. delbrueckii/BLF, L. delbrueckii/HLF and L. gasseri/BLF almost completely blocked the growth of S. aureus on the NA plates.