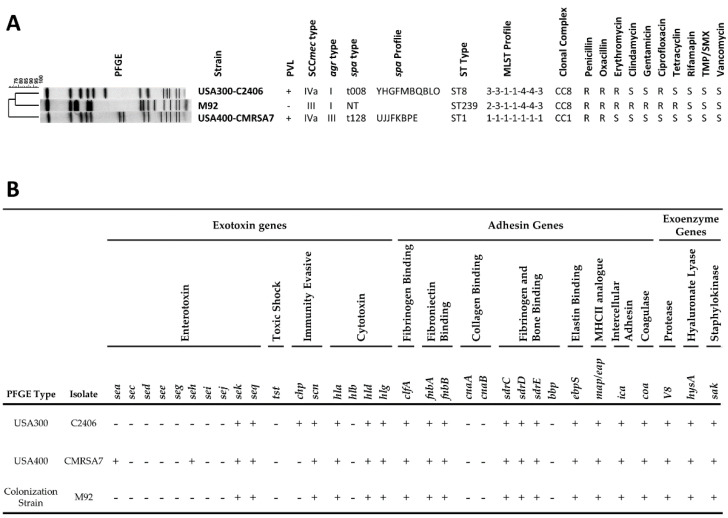
Figure 1.
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) strain genotypic and phenotypic characteristics, and virulence factor profiles. (A) Pulsed Field Gel Elecctrophoresis (PFGE) profiles for the MRSA strains, along with genotypic and phenotypic typing results. PVL, Panton–Valentine leucocidin (+, positive; -, negative); SCCmec, staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec; agr, accessory gene regulator; spa, staphylococcal protein A (non-typable, NT); MLST, multilocus sequence type; CC, clonal complex; S, susceptible; R, resistant. (B) Virulence gene profiles show that the isolates differ by only 3 genes (sea, seh, chp). sea/c/d/e/g/h/i/j/k/q, staphylococcal enterotoxin A/C/D/E/G/H/I/J/K/Q; tst, toxic shock syndrome toxin; chp, chemotaxis inhibitory protein; scn, staphylococcal complement inhibitory protein; hla/b/d/g, α/β/𝛿/γ-hemolysin; clfA, clumping factor; fnbA/B, fibronectin adhesive molecule A/B; cnaA/B, collagen adhesive molecule A/B; sdrC/D/E, putative adhesin; bbp, bone sialoprotein adhesin; ebpS, elastin adhesin; map, major histocompatibility complex class II analog protein; ica, polysaccharide intercellular adhesin. coa, coagulase; V8, serine protease; hysA, hyaluronidase; sak, staphylokinase; +, positive; -, negative.