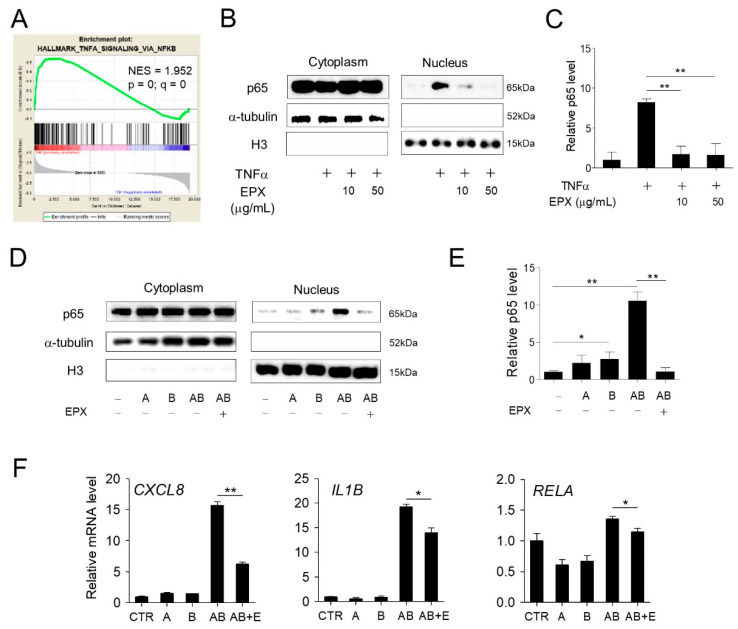
Figure 5.
Eggplant extract inhibits the NF-κB pathway activated by blue light (BL) in RPE cells. (A) GSEA showing that the genes modulated by BL and A2E were significantly enriched in the NF-κB pathway. NES—normalized enrichment score. (B) Inhibition of NF-κB signaling by EPX. EPX inhibited the nuclear translocation of p65 induced by TNFα in ARPE-19 cells. The p65 protein level in the cytoplasm or nuclear fraction was determined by western immunoblot using a specific anti-p65 antibody. α-tubulin and histone H3 were used as internal controls for cytoplasmic and nuclear fractions, respectively. H3—histone H3; TNF—tumor necrosis factor; EPX—eggplant extract; + —sample treatment. (C) Quantification of p65 level in the nucleus. The nuclear p65 level was quantified using ImageJ. The nuclear protein level of p65 was normalized to histone H3 level. The results are presented as the mean ± S.D. (n = 3) (D,E) The effect of EPX on A2E+BL-induced NF-κB pathway. EPX (25 μg/mL) inhibited the translocation of p65 induced by BL in A2E-laden ARPE-19 cells. p65 protein level was determined and quantified, as illustrated in Figure 5B,C. A—A2E; B—blue light; AB—A2E+blue light. (F) The effect of EPX (25 μg/mL) on the expression of pro-inflammatory genes determined by RT-qPCR. The mRNA levels were normalized to 18S rRNA level. CXCL8—C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 8; IL1B—interleukin 1 beta; RELA—proto-oncogene, NF-κB subunit. E—eggplant extract. The results are presented as the mean ± S.D. (n = 3); * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01.