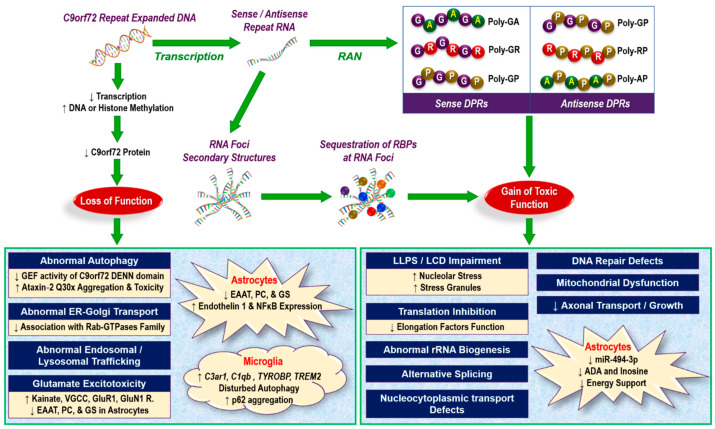
Figure 3.
Pathogenic mechanisms implicated in C9orf72 ALS/FTD. Both loss and gain of function mechanisms contribute to the disease process in C9orf72 ALS/FTD. Abbreviations: ADA, adenosine deaminase; C1qb, complement component 1, Q subcomponent, β polypeptide; C3ar1, complement component 3a receptor 1; DENN, differentially expressed in normal and neoplastic cells; EAAT, excitatory amino-acid transporter; GEF, GEF, guanine nucleotide exchange factor; GluN1 R, glutamate ionotropic receptor NMDA type subunit 1; GluR1, glutamate ionotropic receptor AMPA type subunit 1; GS, glutamine synthetase; LCD, low complexity domain; LLPS, liquid–liquid phase separation; miRNA, microRNA; PC, pyruvate carboxylase; rRNA, ribosomal RNA; TREM2, triggering receptor expressed on myeloid Cells 2; TYROBP, tyrosine kinase binding protein; and VGCC, voltage-gated calcium channel.