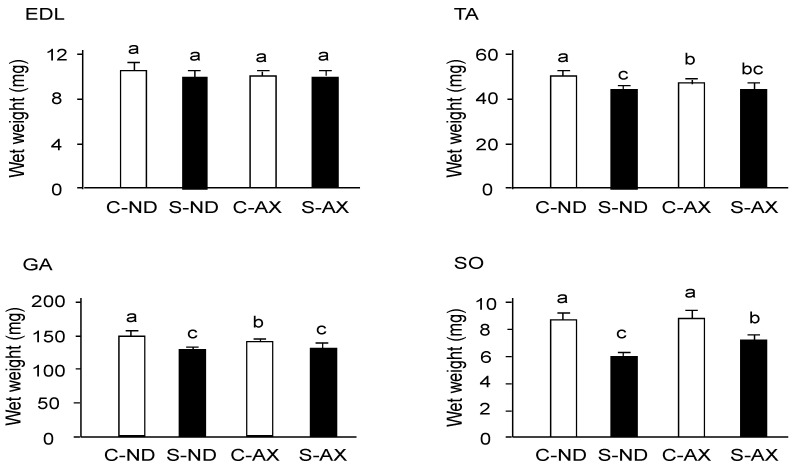
Figure 2.
The effect of dietary AX on muscle mass in tail-suspension mice. An AX-supplemented or normal diet was given to the mice for 4 weeks and their skeletal muscles were isolated 2 weeks after tail suspension. The wet weights of the tibialis anterior, extensor digitorum longus, gastrocnemius, and soleus muscles were measured. Data are presented as mean ± S.D. (n = 6). Different letters indicate significant differences (p < 0.05) based on the two-way ANOVA and Tukey’s test. C-ND, control mice fed the normal diet; S-ND, tail-suspension mice fed the normal diet; C-AX, control mice fed the AX diet; and S-AX, tail-suspension mice fed the AX diet. TA, tibialis anterior muscle; EDL, extensor digitorum longus muscle; GA, gastrocnemius muscle, SO, soleus muscles.