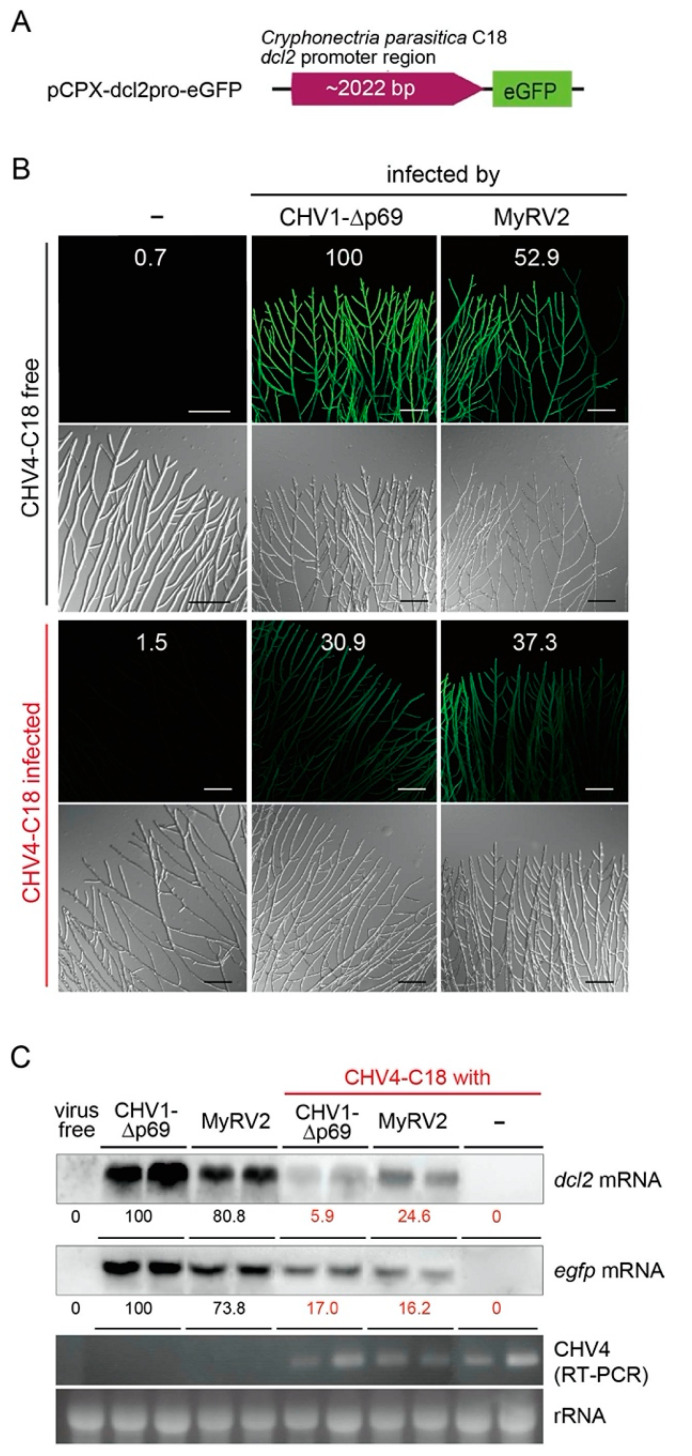
Figure 1.
CHV4 suppresses antiviral RNA silencing via inhibiting dcl2 transcriptional upregulation. (A) The organization of a reporter constructs pCPXHY-C18-dcl2pro::egfp. An egfp gene fused with a 2.2 kbp C. parasitica C18 genomic sequence containing the dcl2 promoter region was cloned into pCPXHY1 and used to transform a virus-free isogenic isolate of C. parasitica C18 strain (C18-VF) [28]. (B,C) CHV4-mediated suppression of the GFP reporter induction. The reporter fungal strain with pCPXHY-C18-dcl2pro::egfp (C18/dcl2pro-eGFP) was infected by CHV1-∆p69 and MyRV2 (B), which are strong dcl2 triggers, or CHV4 and CHV1 wild type (C). Values in the respective panels of (B) show the relative intensity of the reporter eGFP green fluorescence quantified by ImageJ, with the CHV1-∆p69-infected strain expressed as 100. Total RNA fractions were obtained from two biological replicates of the reporter fungal strain (C18/dcl2pro-eGFP) infected by each virus, and subjected to northern blotting to monitor dcl2 and egfp transcript levels. Hybridization and probe preparation are described in the Materials and Method section. Mean values of band intensity in the northern blots (C) quantified by ImageJ are shown below each blot. RT-PCR detection for CHV4 infection or dsRNA electrophoretic gel analysis for MyRV2 (viral dsRNA genome) or CHV1 and CHV1-∆p69 (viral replicative dsRNA form) infection in the reporter fungal strain were conducted. Ribosomal RNA (28S rRNA) was used as a loading control.