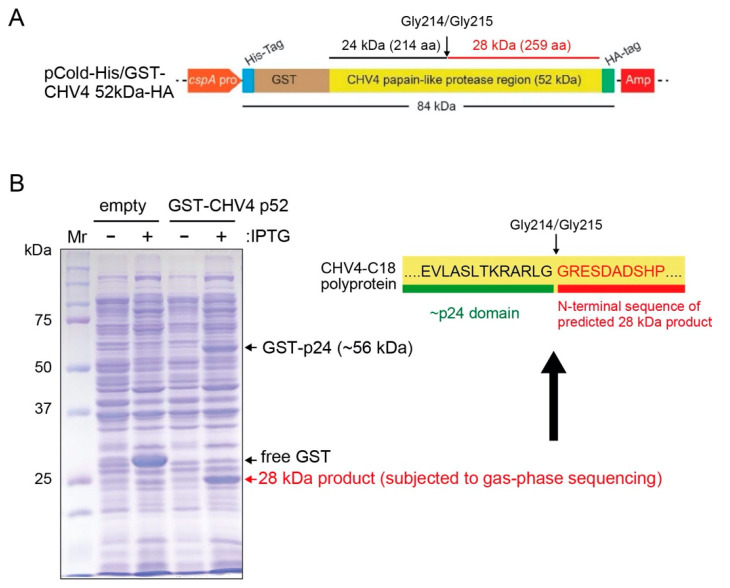
Figure 3.
Autocatalytic proteolytic activity of CHV4 p24 encoded at the most N terminal portion of the viral polyprotein. (A) Schematic representation of the N terminal portion of the CHV4-C18 polyprotein. The N-terminal coding regions spanning amino acids 1 to 473 (the estimated molecular weight of ~ 52 kDa) was cloned into the KpnI-NdeI site of an Escherichia coli expression vector, pCold. The 52kDa coding region was fused in frame with a His-tag and GST at the N-terminus and an HA-tag at the C-terminus (pCold-His/GST-CHV4 52kDa-HA, 86 kDa). The predicted cysteine and histidine residues and di-glycine are shown on the top. (B) The self-cleavage activity of CHV4-C18 p24 in the recombinant E. coli cells. Total proteins in E. coli cells transformed by the CHV4-52kDa expression construct and empty vector were electrophoresed in SDS-PAGE gel and stained with Coomassie Brilliant Blue. Two protein bands of 52kDa and 28 kDa were specifically induced in the recombinant cells with the CHV4-52kDa construct upon induction (left panel, shown with arrows). Unpurified fractions of the over-expressed protein encoded by the N terminal portion of CHV4 were blotted onto PVDF membrane, and the 28 kDa protein band was subjected to chemical sequencing. The six determined amino acid residues were the same as those deduced from the CHV4 nucleotide sequence. The cleavage site was experimentally identified as Gly245↓Gly246, which had been predicted by Linder-Basso et al. [41].