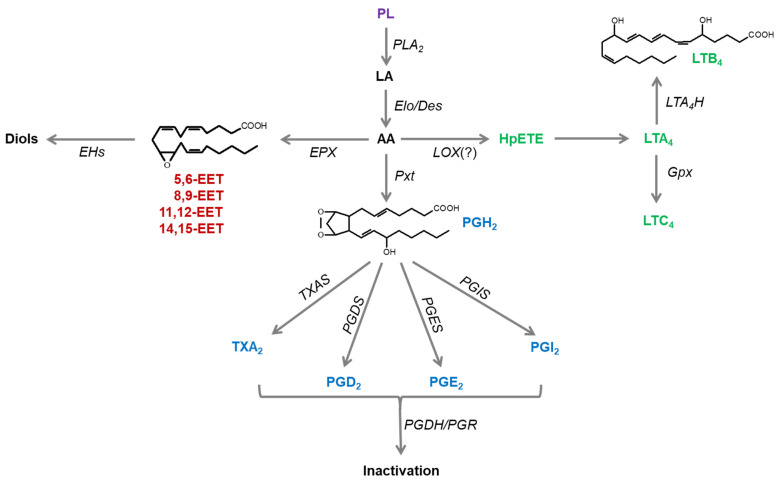
Figure 1.
Eicosanoid biosynthesis and degradation in insects. Phospholipase A2 (PLA2) catalyzes hydrolysis of linoleic acid (LA) from membrane-associated phospholipids (PLs), which is elongated by long-chain fatty acid elongase (Elo) and desaturated by desaturase (Des) to arachidonic acid (AA). AA is then oxygenated by epoxidase (EPX) into epoxyeicosatrienoic acid (EET), lipoxygenase (LOX) into leukotriene (LT), or cyclooxygenase-like peroxynectin (Pxt) to prostaglandin (PG). EETs are degraded by soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH). LTA4 is formed from 5-hydroxyperoxide eicosatetraenoic acid (HpETE) and changed into LTB4 by LTA4 hydrolase (LTA4H) or into LTC4 by glutathione peroxidase (Gpx). Various PGs are formed from PGH2 by cell-specific enzymes, thromboxane A2 (TXA2) synthase (TXAS), PGD2 synthase (PGDS), PGE2 synthase (PGES) and PGI2 synthase (PGIS). These PGs are degraded by PG dehydrogenase (PGDH) and PG reductase (PGR).