Figure 3.
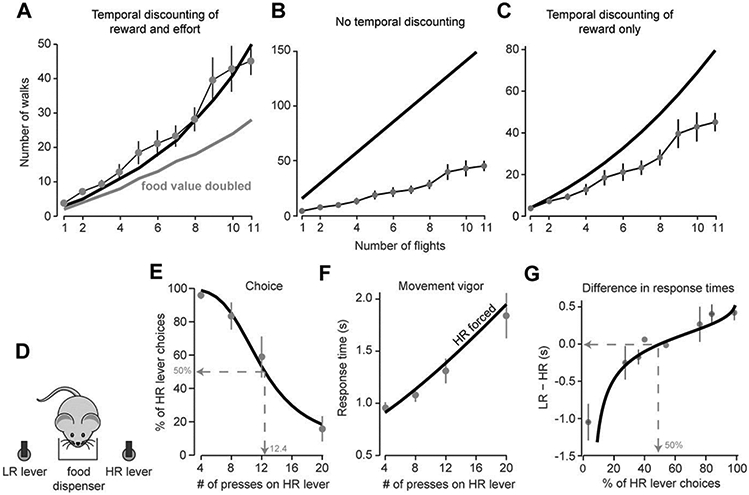
Top panel: decision-making in birds in an experiment in which the objective values of reward, and the metabolic cost of the movements, are both known. A. Birds chose between flying nf number of times, and walking nw number of times, to receive a reward. The data points represent the indifference values, computed from the choices that the animals made 16. The solid curve is the predicted indifference curve for the utility function in which both reward and metabolic cost were discounted by duration of the movements. The gray curve is the predicted indifference if the food value were doubled (the animals would we willing to fly more often). B. Predictions of a utility in which neither reward nor metabolic costs are discounted by duration of the movement. C. Predictions of a utility in which only reward is discounted by duration of the movement. Bottom panel: Decision-making in rats in an experiment in which they chose between the low-reward (LR) lever (4 presses would produce 2 pellets of food), or high-reward (HR) lever (a variable number of presses would produce 4 pellets of food). D. Schematic of the experimental setup. In choice trials, both options were available. In forced trials, only one option was available. E. Data points are the percent of choice trials in which the animals chose the HR lever, plotted as a function of the number of presses that were required on that lever (data from Walton et al. 9). The curve is the probability of choosing the HR option computed via the difference in the utilities of the two options. F. Response times in the forced trials in which only the HR lever was available. The points are measured data and the curve is the duration predicted by Eq. (16). G. The difference in response times in the force trials between the HR and LR options. The points are measured data and the curve is the difference in duration predicted by the model.
