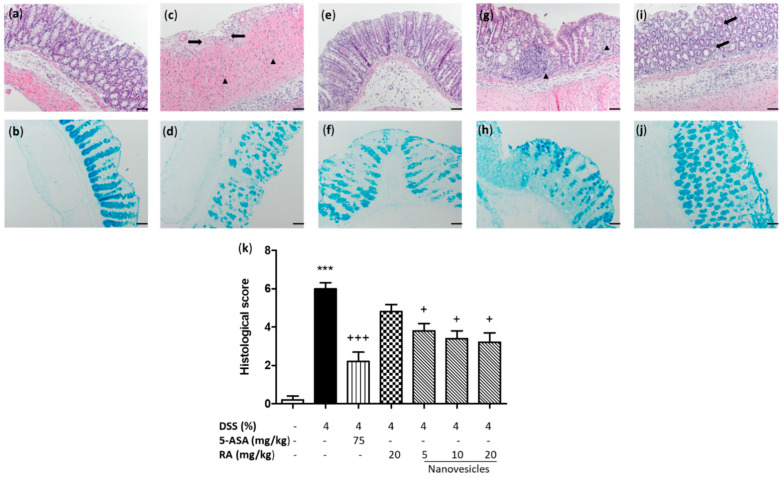
Figure 3.
Rosmarinic acid (RA)-loaded nanovesicles administration attenuated DSS-induced microscopic colon damage and improved mucus accumulation inside the goblet cells. Histological images of colons following haematoxylin and eosin staining and Alcian blue staining: (a,b) sham group; (c,d) DSS group, ulceration (black arrows) and inflammatory cells (black triangle) in the lamina propria; (e,f) aminosalicylic acid (5-ASA) (75 mg/kg), (g,h) RA group (20 mg/kg), abundant inflammatory infiltrate (black triangle) and (i,j) RA-loaded nanovesicles (20 mg/kg, is shown as representative image of all the doses used), mucosal reparation and decrease of inflammatory infiltrate (black arrows). Original magnification 200 X. Scale bar: 50 µm. (k) Histopathological score of the colon was evaluated as indicated in the Methods section. Mean value was significantly different compared with the sham group (*** p < 0.001; Mann–Whitney U test). Mean value was significantly different compared with DSS group (+ p < 0.05, +++ p < 0.01; Kruskal–Wallis test).