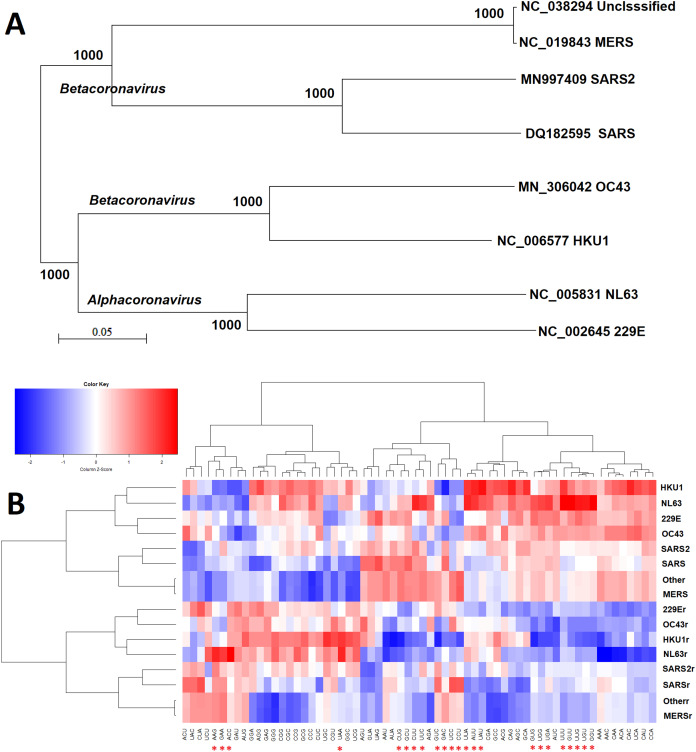
Figure 2. Comparison of sequence and ribonucleotide trimer compositions of coronaviruses infect human hosts.
Comparison of analysis results from the conventional phylogenetic method and the weight triribonucleotide compositions proposed in this study (A) Phylogenetic analysis of full-length genomic sequences of representative coronaviruses infecting human hosts. The number of each branch obtained from 1,000 bootstrapping is shown. The accession numbers indicate the representative genomic sequences used in this analysis. (B) Comparison of triribonucleotide compositions of coronaviruses infecting human hosts. 229E: human coronavirus 229E. NL63: human coronavirus NL63. HKU1: human coronavirus HKU1. OC43: human coronavirus OC43. SARS: severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV), MERS: Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV). SARS2: severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). Other: unclassified coronaviruses. The lowercase r notations indicate the complementary (−) strands of genomic RNAs (replication intermediates). The red stars (*) indicate human TLR 7/8 stimulatory triribonucleotides.