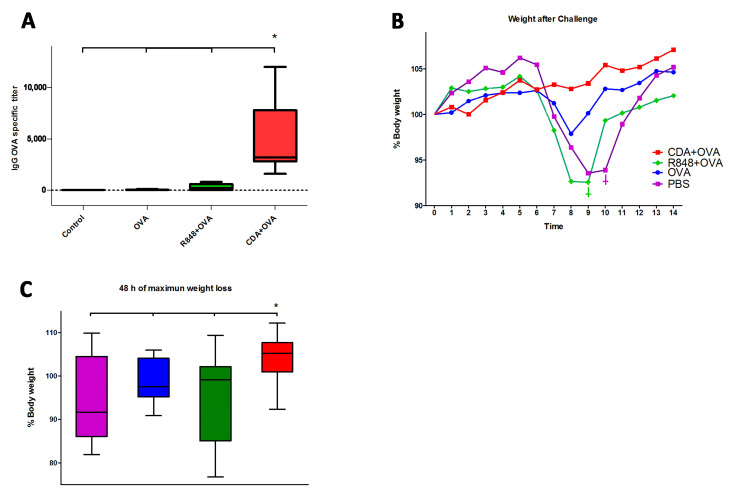
Figure 4.
Neonatal vaccination with CDA confers protection in adult mice. Mice intranasally vaccinated with CDA + OVA, R848 + OVA, OVA, or PBS (control) were challenged by 105 PFU of the H1N1 PR8 influenza A/WSN/33 (WSN)-OVA(I) virus, which expresses the SIINFEKL peptide in the hemagglutinin domain. (A) Antigen-specific IgG from blood serum was measured by ELISA from blood sampled previous to challenge. Mice Vaccinated with CDA + OVA as neonates displayed significantly higher titers than animals receiving the other vaccine formulations. (B) Weight loss was recorded 14 days after infection as an inverse correlation of protection, where dead animals were found only in the PBS and the R848 groups (inverted crosses in plot B). (C) The differences between groups on the 48 h of maximum weight loss were significant between CDA + OVA vaccinated animals and the other treatments. In (A,C) differences are significant (*) by a non-paired Student’s t-test (* p ≤ 0.05) performed against each other treatment/control. Results shown are average from five (PBS and OVA controls) and six (CDA and R848 treatments) mice per group, from one representative out of two experiments.