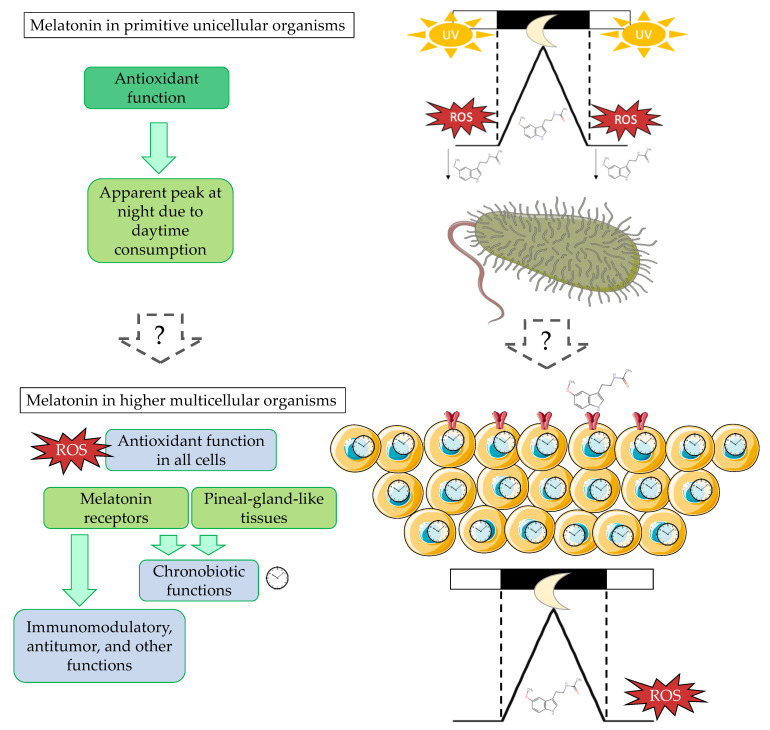
Figure 1.
Melatonin’s biological functions throughout evolution. In primitive unicellular organisms (upper panel), its antioxidant primary function generated an apparent concentration peak at night. Subsequent events drove the appearance of melatonin receptors and pineal gland-like tissues (lower panel), permitting higher multicellular organisms to adopt melatonin as a chronobiotic (darkness) signal while maintaining local extrapineal melatonin production in most organs and tissues, exerting its antioxidant original function. Melatonin in multicellular organisms also presents a wide range of actions, such as immunomodulatory and antitumor, among others. This figure was built with SMART resources (Servier Medical Art) and licensed under a Creative Common Attribution 3.0 Generic License. See http://smart.servier.com/.