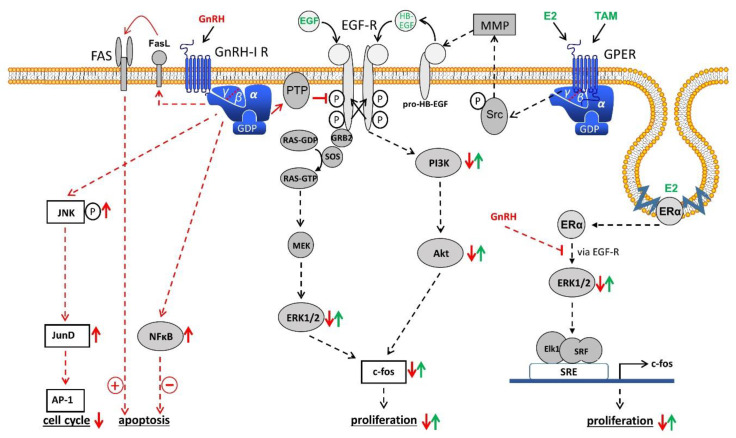
Figure 1.
Gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH) receptor signal transduction in endometrial cancer (EC). Binding of GnRH-I and GnRH-I agonists causes G-protein αi-mediated activation of phospho-tyrosine phosphatase (PTP), resulting in dephosphorylated EGF-receptor (EGF-R) and inhibition of EGF-R signal transduction through the ERK1/2 or the PI3K/AKT pathway leading to a reduction of proliferation. GnRH-induced activation of PTP also inhibits the signaling cascade of G-protein coupled estrogen receptor (GPER) and estrogen receptor α (ERα) through transactivation of EGF-R. In addition, GnRH induces activation of NFκB to reduce and FAS-ligand to increase apoptosis. Finally, GnRH agonists activate the JNK/AP-1 pathway, resulting in an increased G0/1 phase of the cell cycle and decreased DNA-synthesis. Akt, protein kinase B (PKB). AP-1, activator protein-1. E2, estradiol. EGF, epidermal growth factor. ERK1/2, p44/42 mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase. FAS, Fas receptor. FasL, Fas ligand. GDP, guanosindiphosphate. GRB2, growth factor receptor-bound protein 2. GTP, guanosintriphosphate. HB-EGF, heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor. JNK, c-Jun N-terminale kinase. JunD, transcription factor JunD. MEK, mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase (MAP2K). MMP, matrix metalloproteinase. NFkB, nucleus factor kB. PI3K, phosphoinositide 3-kinase. RAS, G-protein rat sarcoma. SOS, guanine nucleotide exchange factor ”son of sevenless“. SRE, serum response element. Src, tyrosine kinase cellular sarcoma. SRF, serum response factor. TAM, tamoxifen.