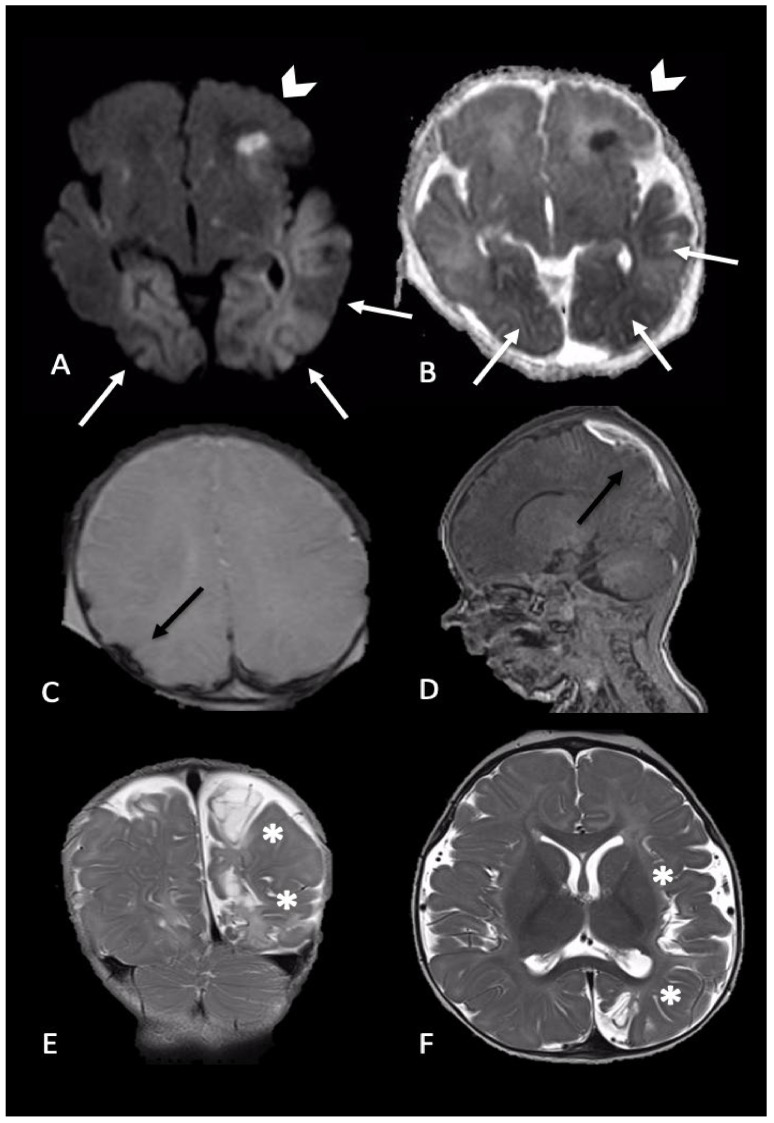
Figure 3.
Newborn reached the emergency department for single episode of apnea followed by generalized seizures. MRI performed 4 days later showed intraparenchymal injuries and bilateral extra-axial mixed-intensity fluid collections. In particular, (A,B) (axial DWI and ADC maps) showed bilateral temporal and occipital cortical areas of restricted diffusion (white arrows) and a focal area of restricted diffusion localized in the left frontal lobe and diffuse (arrows-head), indicative of acute intraparenchymal injury; (C,D) (axial SWI and sagittal T1-W) showed extra-axial blood collection along the parietal convexity bilaterally (black arrows). Six-month follow-up MRI ((E,F), coronal and axial T2-W) revealed malacic evolution of intraparenchymal damage and consequent expansion of extra-axial spaces due to tissue loss (asterisks).