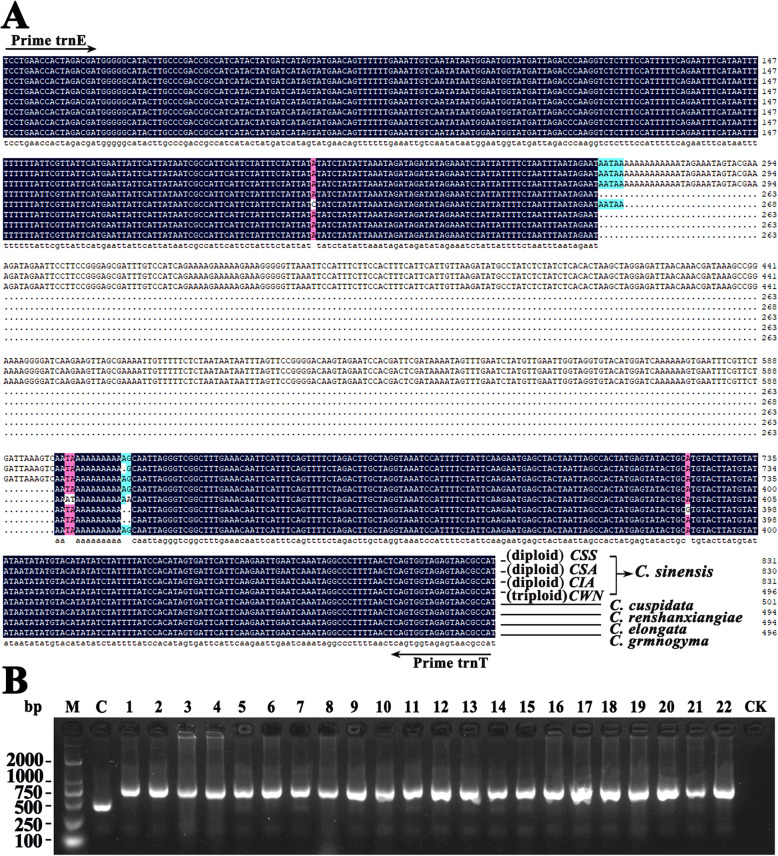
Fig. 11.
Analysis of cp sequence characterized amplified region (SCAR) using a 335 bp deletion of the intergenic spacers (trnE/trnT). a By comparing with the cp genomes of three representative diploid C. sinensis species, a 335 bp long deletion was observed in triploid CWN, and the similar long deletion could be found in four other Camellia species, including: C. cuspidate, C. renshanxiangiae, C. elongata and C. gymnogyna. The shadow Blue mean homology = 100%, pink mean homology≥70%, turquoise mean homology≥50% and the dot indicated missing. The number on the right showed the sequence length. The position of the primers was indicated by the arrow. b Only PCR products of CWN had a 335 bp long sequence deletion, while those of other 292 C. sinensis did not. M: D2000 DNA molecular marker; c PCR products of CWN; Lane 1–22: PCR products of 22 examples of randomly selected cultivars from 292 different cultivars covering the majority of C. sinensis cultivars in China. CK: Control. All 292 PCR products were shown in Supplementary Fig. S1. CWN: ‘Wuyi narcissus’ cultivar of C. sinensis var. sinensis (natural triploid Chinary type tea); CSS: C. sinensis var. sinensis (diploid Chinary type tea); CSA: C. sinensis var. assamica (diploid Chinese Assamica type tea); CIA: C. sinensis var. assamica (diploid Indian Assamica type tea)