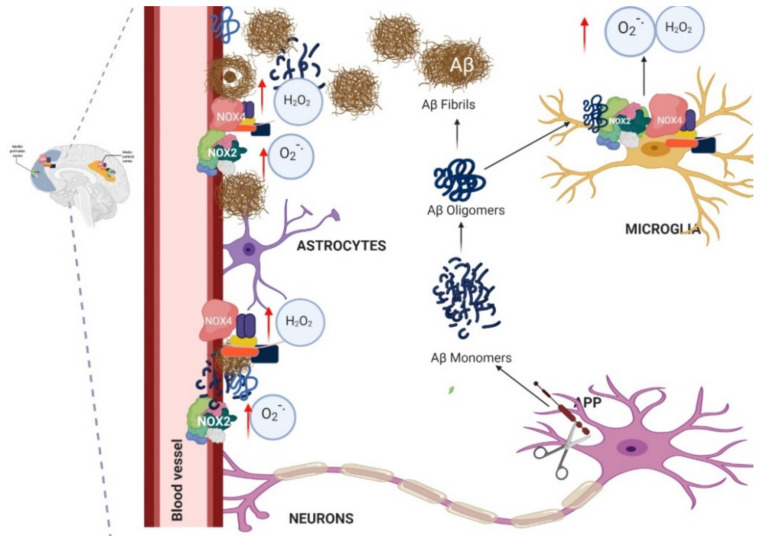
Figure 5.
NOX2 and NOX4 in the brain and in the vasculature. NOX2 and NOX4 are the principal isoforms of NOX in the brain, and which participates in Alzheimer’s disease (AD). NOX2 and NOX4 are found in the brain cells (microglia, astrocytes, neurons, etc.) and also in endothelial cells of the vasculature in the brain. Then, when amyloid beta (Aβ) is produced from APP, the monomers and then the oligomers and fibrils are formed, and these Aβ aggregates can go to the blood vessel wall and produce neurovascular dysfunction, which is also secondary to the incomplete clearance of Aβ. In addition, the activation of NOX2 and NOX4 by Aβ oligomers can occur in brain cells to increase neurotoxins and reactive oxygen species (ROS), contributing to the neurotoxicity, cognitive deficit and dementia.