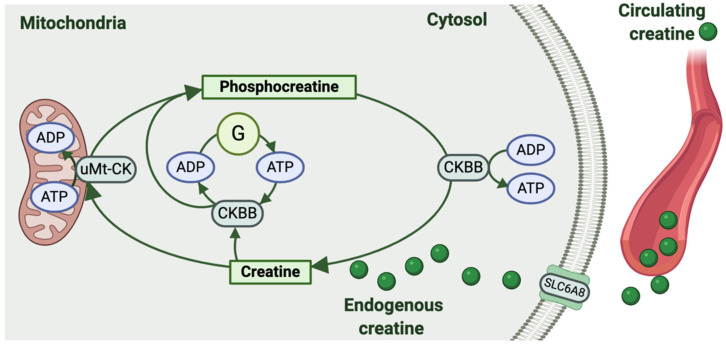
Figure 1.
The creatine kinase circuit. Creatine can be produced endogenously by some cells or taken up from the circulation via the creatine transporter (SLC6A8). Creatine is then phosphorylated from adenosine triphosphate (ATP) to form phosphocreatine and adenosine diphosphate (ADP) in a reaction catalyzed by ubiquitous mitochondrial creatine kinase (uMt-CK). Isoforms of creatine kinase in the cell cytosol (mainly brain-type creatine kinase CKBB) are also linked to glycolytic enzymes (G) to generate phosphocreatine and ADP from glycolytic ATP. Then, when required for energy-dependent cellular processes, cytosolic isoforms of creatine kinase (CKBB) hydrolyze the bond between creatine and the phosphate group stored as phosphocreatine, thus regenerating ATP and creatine. Note: muscle-type cytosolic creatine kinase (CKMM) expression has also been detected in mouse oocytes.