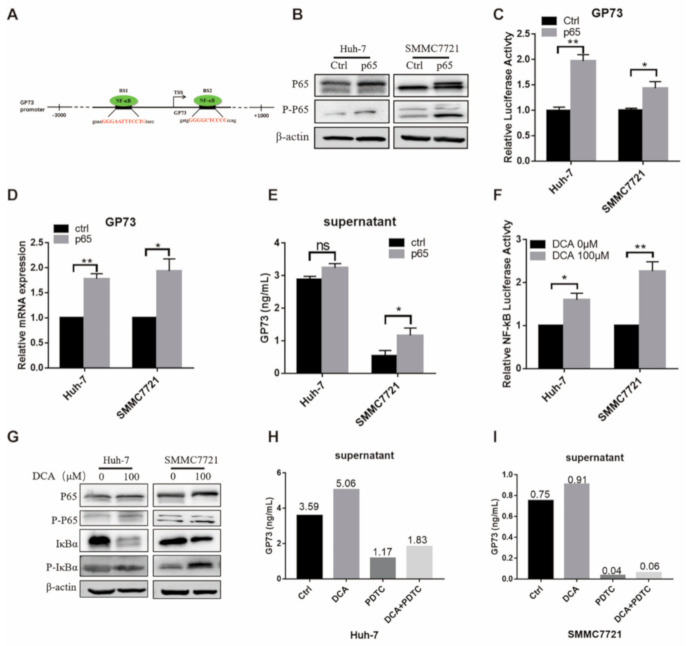
Figure 3.
Deoxycholic acid (DCA) upregulates the expression of endogenous Golgi protein 73 (GP73) through activation of the NF-κB pathway. (A) Schematic diagram of NF-κB binding sites on GP73 promoter. (B–D) Huh-7 and SMMC7721 cells were transfected with PCMV-p65 or control PCMV vectors for 72 h. Samples were collected and a Western blot assay of NF-κB P65 and P-P65 (B), detection of cell supernatant level of GP73 by ELISA (C), and qRT-PCR assay of GP73 mRNA level (D) were performed. (E) Huh-7 and SMMC7721 cells were transfected with PGL3-GP73 together with control vector PCMV or PCMV-p65. Luciferase activities were measured 48 h later. (F) Huh-7 and SMMC7721 cells were transfected with an NF-κB-dependent firefly luciferase construct and treated with 100 μM DCA. Samples were harvested 48 h after treatment, and luciferase activities were measured. (G) Huh-7 and SMMC7721 cells were treated with 100 μM DCA for 72 h. NF-κB pathway proteins were determined by Western blot assay. Cell supernatant levels of GP73 in Huh-7 (H) and SMMC7721 (I) cells exposed to 0.1% dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO, ctrl) (Ctrl), 100 μM DCA, 50 μM pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate (PDTC), or 100 μM DCA plus 50 μM PDTC were detected by ELISA. Data in (C–F) are expressed as the mean ± SEM and represent three independent experiments (* p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001; ns: not significant). Statistical analysis was performed using GraphPad Prism7.