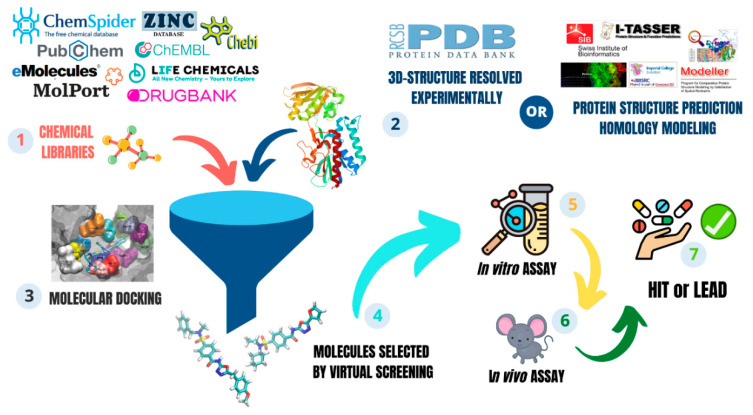
Figure 3.
Drug design by in silico approaches. This process can be divided into at least seven steps. (1) Prepare the molecules libraries with filters such as Lipinski’s rule. Currently different databases are commercially available: https://www.molport.com/shop/index; http://www.chemspider.com/; https://zinc.docking.org/; https://www.ebi.ac.uk/chebi/; https://reaxys.emolecules.com/index.php; https://go.drugbank.com/; https://www.ebi.ac.uk/chembl/; https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/; https://lifechemicals.com; (2) Prepare the target protein, either from the experimentally solved protein database (https://www.rcsb.org/) or by homology modeling (https://salilab.org/modeller/; https://zhanglab.ccmb.med.umich.edu/I-TASSER/; http://www.expasy.org/resources/swiss-model; https://robetta.bakerlab.org/; https://www.schrodinger.com/prime; (3) Analyze the in silico data in search of new molecules (4) Perform the experiments in vitro; (5) Analyze the results in vitro to start point (6) in vivo experiments; (7) Compounds that meet all the requirements can sequence with the hit-to-lead process.