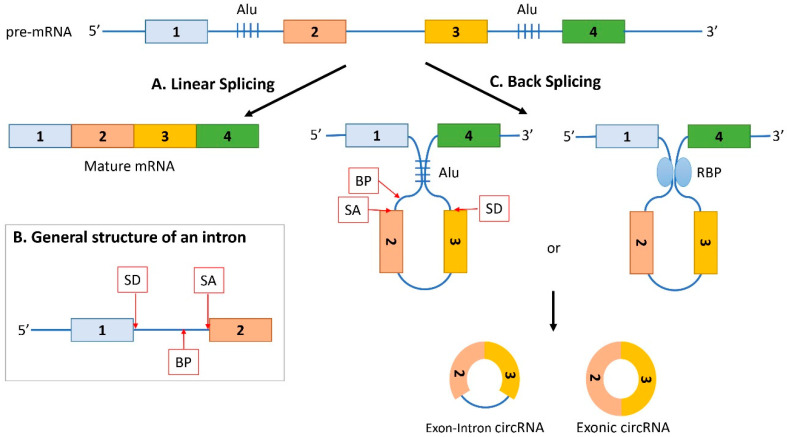
Figure 1.
Generation of circRNAs by back splicing. (A) The immature pre-mRNA undergoes linear splicing where introns are removed, and exons are linearly joined to form the mature mRNA. (B) Introns contain different important sites for the splicing reaction: The splice-donor site (SD) at the 5’ left end, the splice-acceptor site (SA) at the 3’ right end, and the branch point (BP). (C) The immature pre-mRNA undergoes back splicing when there is a formation of a loop between the intron sequences flanking the downstream SD site and the upstream SA site. The formation of the loop is promoted by base pairing between inverted repeat elements of the flanking introns, such as Alu elements (Alu) or by the dimerization of RNA-binding proteins (RBP) that specifically bind to the flanking introns. Consequently, an upstream BP extends to a downstream SD site and allows the formation of a covalent binding between the 5′ site of an upstream exon and the 3′ end of a downstream exon, creating an Exon-Intron circRNA. If the intron is spliced-out from a transient Exon-Intron circRNA, or the covalent binding occurs between the 5′ site of an exon with the 3′ of the same exon, an Exonic circRNA originates.