Fig. 5.
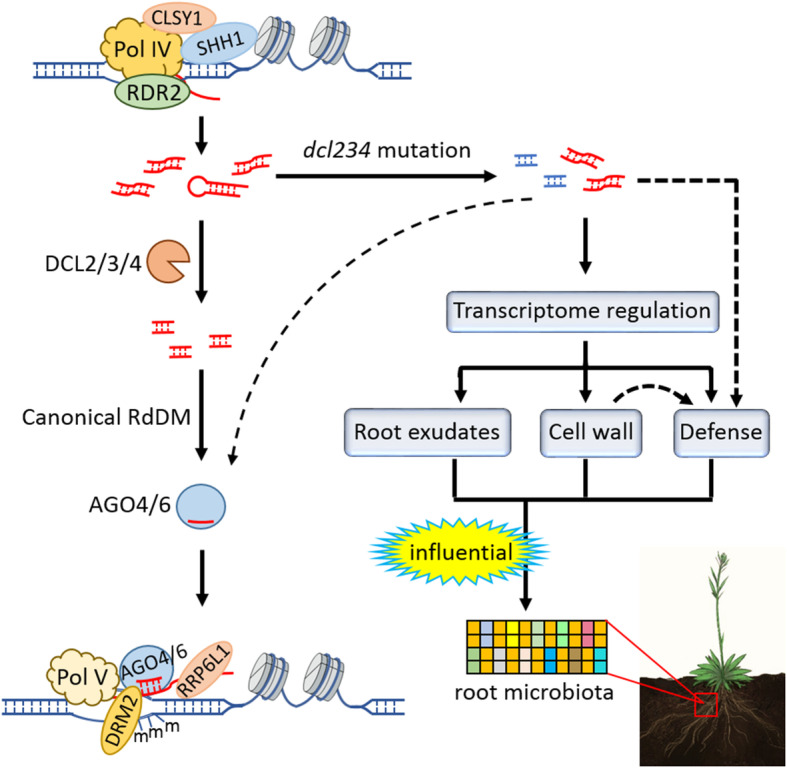
A schematic model depicting the functional mechanism underlying the impacts on root microbiota by the dcl234 triple mutation. In the canonical RdDM pathway, Arabidopsis DCL2, DCL3, and DCL4 function in continuum to regulate the biogenesis of 21–24 nt siRNAs, whose precursors originate from Pol IV-dependent transcription. In wild-type Arabidopsis, the canonical RdDM pathway shows no connection with the assembly of root microbiota. In the dcl234 triple mutant, the disrupted sRNA homeostasis leads to multilayered alterations in several biological processes that are important for plant-microbe interactions, including defense-related gene expression, cell wall modifications, and root exudation of metabolites, which are concomitant with an altered root microbiota assembly. Dashed arrows indicate potential effects (see the main text for details). Besides the dcl234 triple mutant, the RdDM mutants (with the corresponding gene names in parentheses) investigated in this study include nrpd1-3 (Pol IV), nrpe1-11 (Pol V), rrp6l1-2 (RRP6L1), and ddc (DRM1, DRM2, CMT3). In addition to the examined factors, several other RdDM components are also shown [24], including CLSY1 (CLASSY 1), SHH1 (SAWADEE HOMEODOMAIN HOMOLOGUE 1), RDR2 (RNA-DEPENDENT RNA POLYMERASE 2), AGO4 (ARGONAUTE 4), and AGO6. For simplicity, not all known RdDM components are shown
