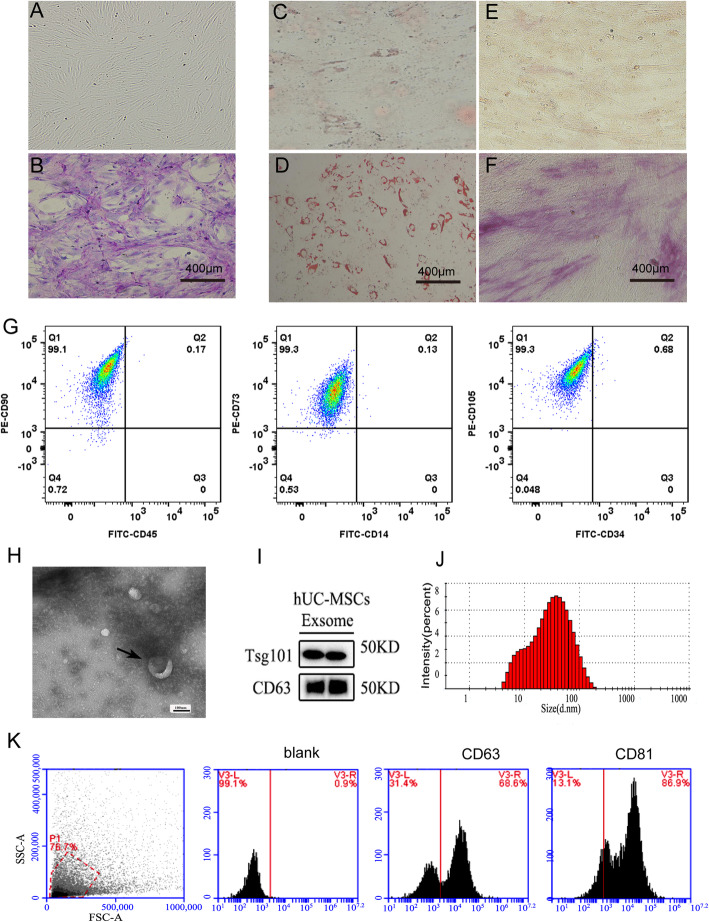
Fig. 1.
Identification of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell (huc-MSCs)-derived exosomes. Nucleated cells isolated from umbilical cord displayed a fibroblast-like morphology (a). The adherent cells (P3) were stained with Wright-Giemsa (b). Adipogenesis differentiation was indicated by the presence of lipid drops that stained with Oil Red O (c and d; c control; d experimental group). Osteogenic differentiation was shown by intracytoplasmic accumulation of alkaline phosphatase (e and f, e control; f experimental group). The phenotype of huc-MSCs was detected by flow cytometry. CD45, CD34, and CD14 were negative while CD73, CD105, and CD90 were positive (g). huc-MSCs-Exo (marked by the black arrows) were observed under electron microscopy (h). Exosome-specific markers (e.g., TSG101 and CD63) were positive by Western blot analysis (i). NanoSight analysis indicated that particle size of MSCs-Exo was 30–100 nm (j). Analysis of exosome-specific markers CD81 and CD63 was positive by flow cytometry (k)