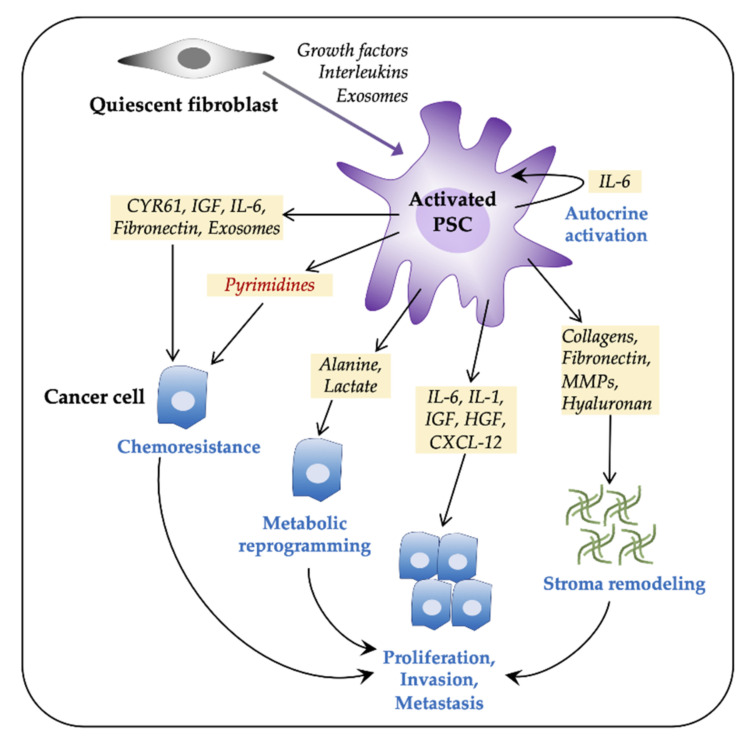
Figure 1.
Pancreatic stellate cells (PSCs) facilitate tumor progression in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC). Pancreatic tumors consist of a large number of activated fibroblasts, which are myofibroblast-like cells and are referred to as PSCs. Fibroblasts are activated by both paracrine and autocrine signals. Activated PSCs promote cancer cell proliferation, invasiveness, metastasis, and chemoresistance via various paracrine, exosome-mediated, or autophagic mechanisms. PSCs contribute to tumor progression by metabolic reprogramming and by extracellular matrix components-mediated stromal remodeling. CXCL12, C-X-C motif chemokine 12; CYR61, cysteine-rich angiogenic inducer 61; HGF, hepatocyte growth factor; IL, interleukin; IGF, insulin-like growth factor; MMPs, matrix metalloproteinases; PDAC, pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.