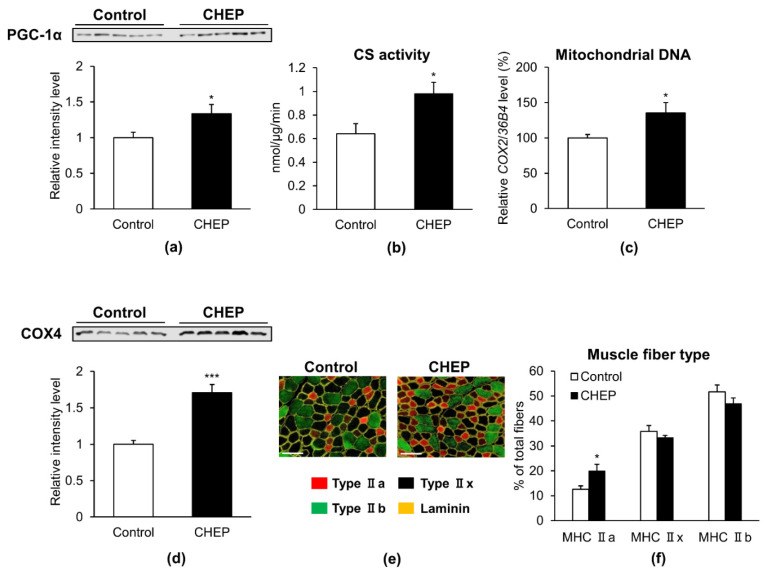
Figure 2.
CHEP increases the amount of PGC-1α protein, mitochondria, and oxidative fibers in murine skeletal muscle. Seven-week-old male C57BL/6J mice were treated with an HC diet (control) or an HC diet containing 0.25% (w/w) CHEP for 5 weeks. Protein expression levels of PGC-1α (a) and COX4 (d) in the gastrocnemius were evaluated using western blotting. Total PGC-1α and COX4 protein levels were normalized to the total protein amount on the membrane, obtained after Ponceau S staining. Relative protein levels were expressed compared to those of the control. (b) CS activity in the gastrocnemius was normalized to protein content in the homogenate. (c) Mitochondrial DNA content in the gastrocnemius is expressed as a percentage relative that in control. Relative mitochondrial DNA copy number was calculated as the ratio of COX2 (mitochondrial) to 36B4 (nuclear) gene expression level, using real-time PCR. (e) Representative images of TA stained with anti-MHC type IIa (red), type IIb (green), and laminin (yellow) antibodies. Unlabeled fibers (black) are MHC IIx fibers. There are no MHC I (blue) fibers in this section. Scale bar: 100 μm. (f) Percentage of muscle fiber types in TA. Muscle fibers were counted in all cross sections based on immunofluorescence staining. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM (n = 5); * p < 0.05, *** p < 0.001 vs. control. HC, high carbohydrate; COX4, cytochrome c oxidase subunit IV; TA, tibialis anterior; MHC, myosin heavy chain.